多模态(Multimodal) 及 多模态大语言模型(MLLMs) 学习笔记
多模态基础 | Multimodal
Keywords:
- 早期
- VLP(Vision-and-Language Pre-training) | “视觉-语言”预训练
- VLMs(Vision Language Models) | 视觉语言模型
- 当前:
- Multimodal Pre-training | 多模态预训练
Architectures:
- dual-encoder | 双编码器
- 适合理解任务,侧重模态特征提取(Features Extraction)
- eg: CLIP
- encoder-decoder | 编码器-解码器
- 适合生成任务,侧重模态交互(Modality Interaction)
- eg: SimVLM, AlBeF, BLIP
- fusion-encoder | 混合编码器
- eg: ViLT, VLMo, BEiT-3
Tasks:
- Vision
- Language
- Vision-Language
Tutorials
Milestones
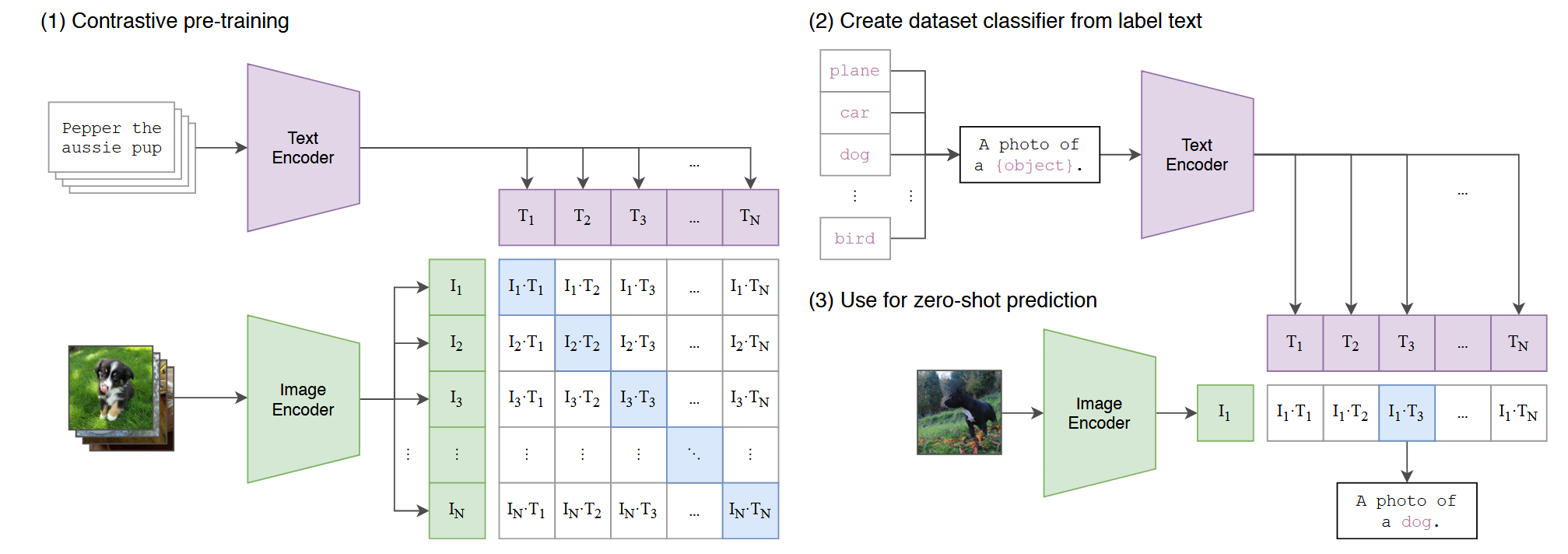
CLIP (2102)
Learning Transferable Visual Models From Natural Language Supervision
https://arxiv.org/abs/2103.00020

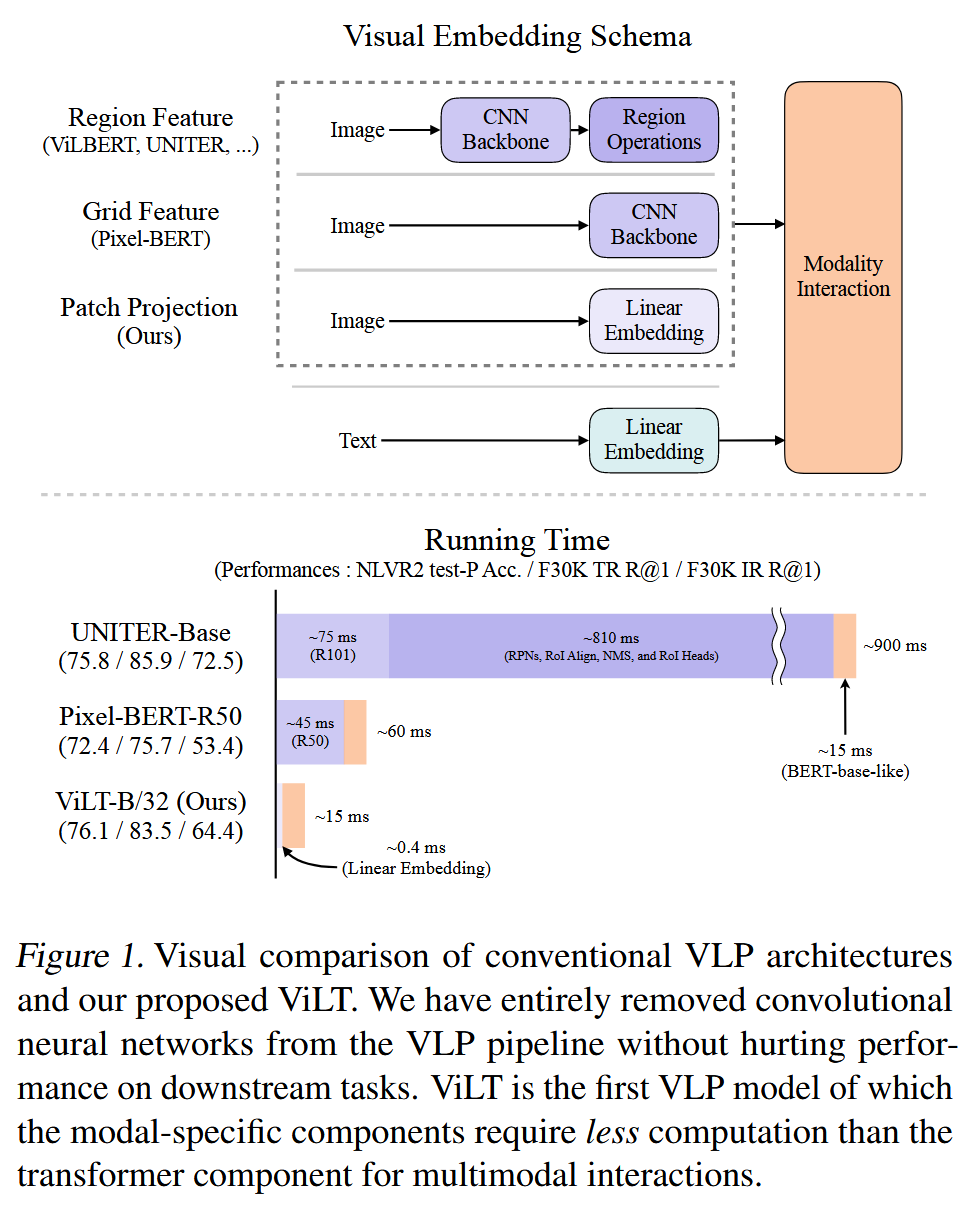
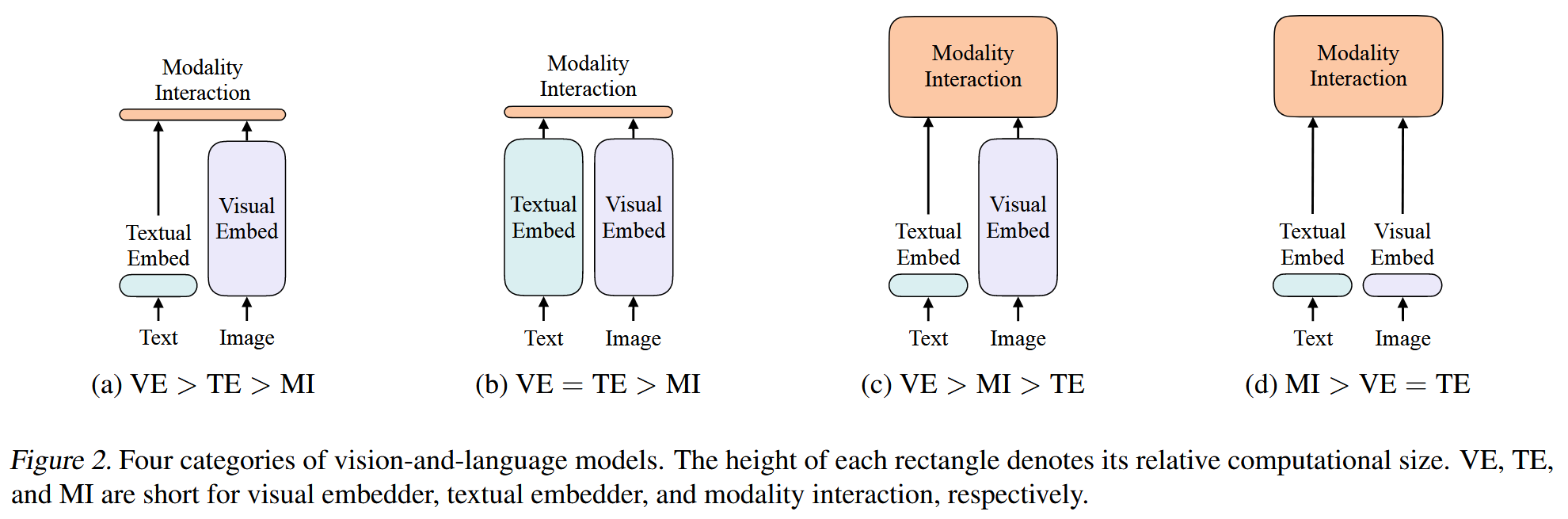
ViLT (2102)
ViLT: Vision-and-Language Transformer Without Convolution or Region Supervision
https://arxiv.org/abs/2102.03334
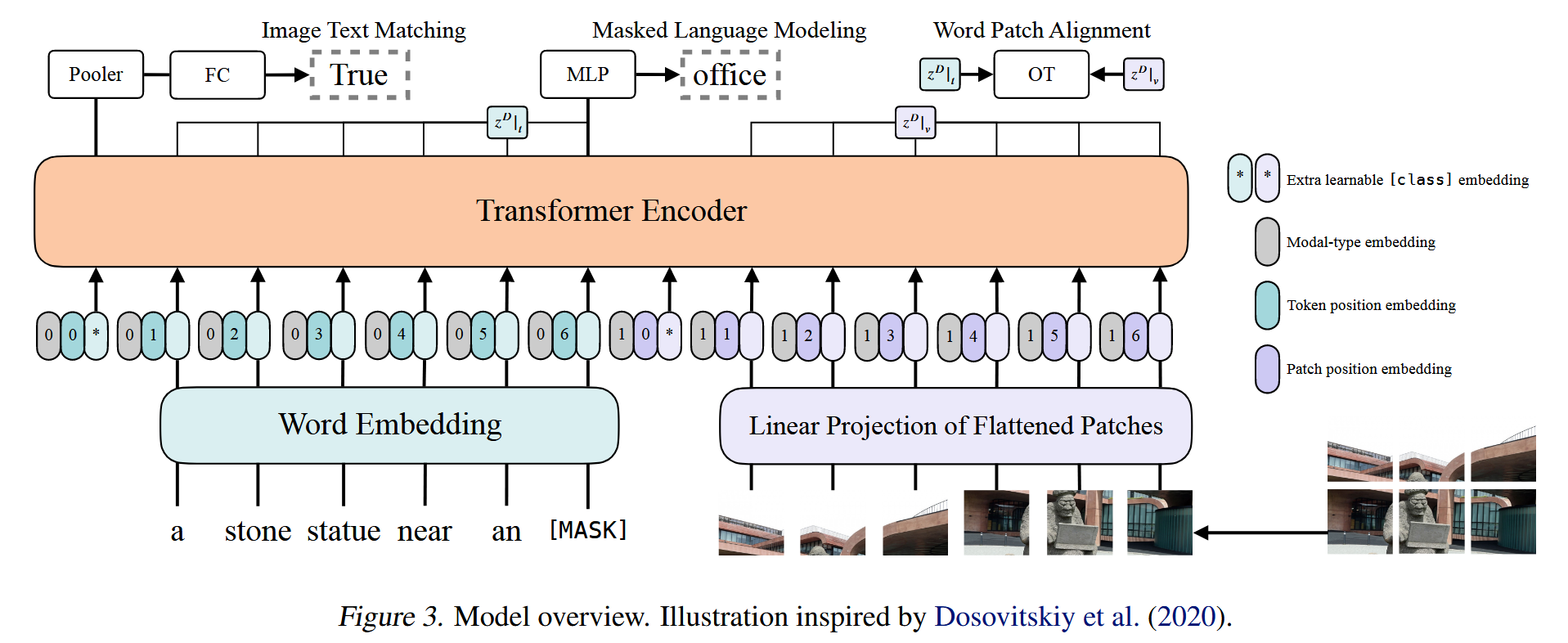
AlBeF (2107)
Align before Fuse: Vision and Language Representation Learning with Momentum Distillation
https://arxiv.org/abs/2107.07651
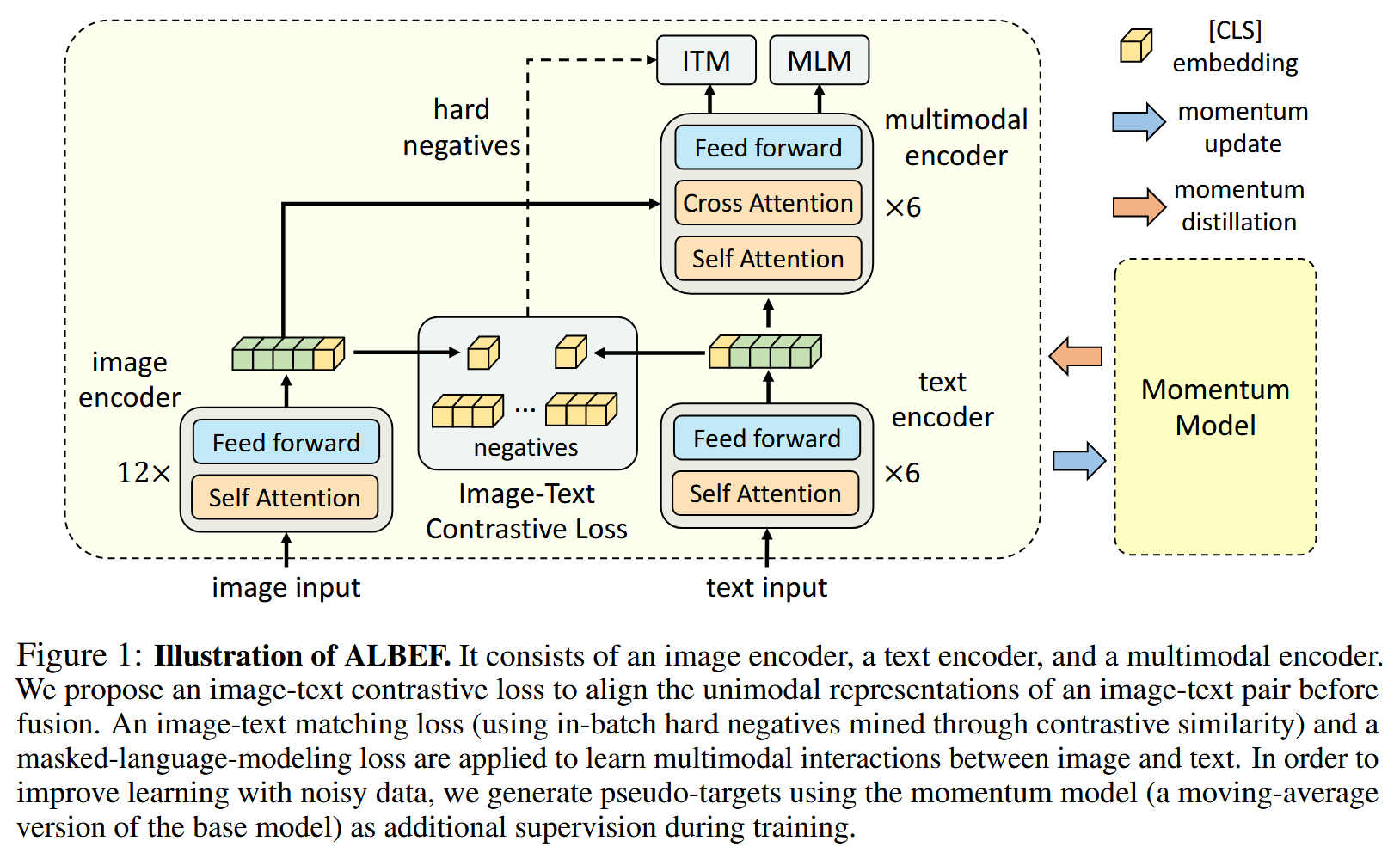

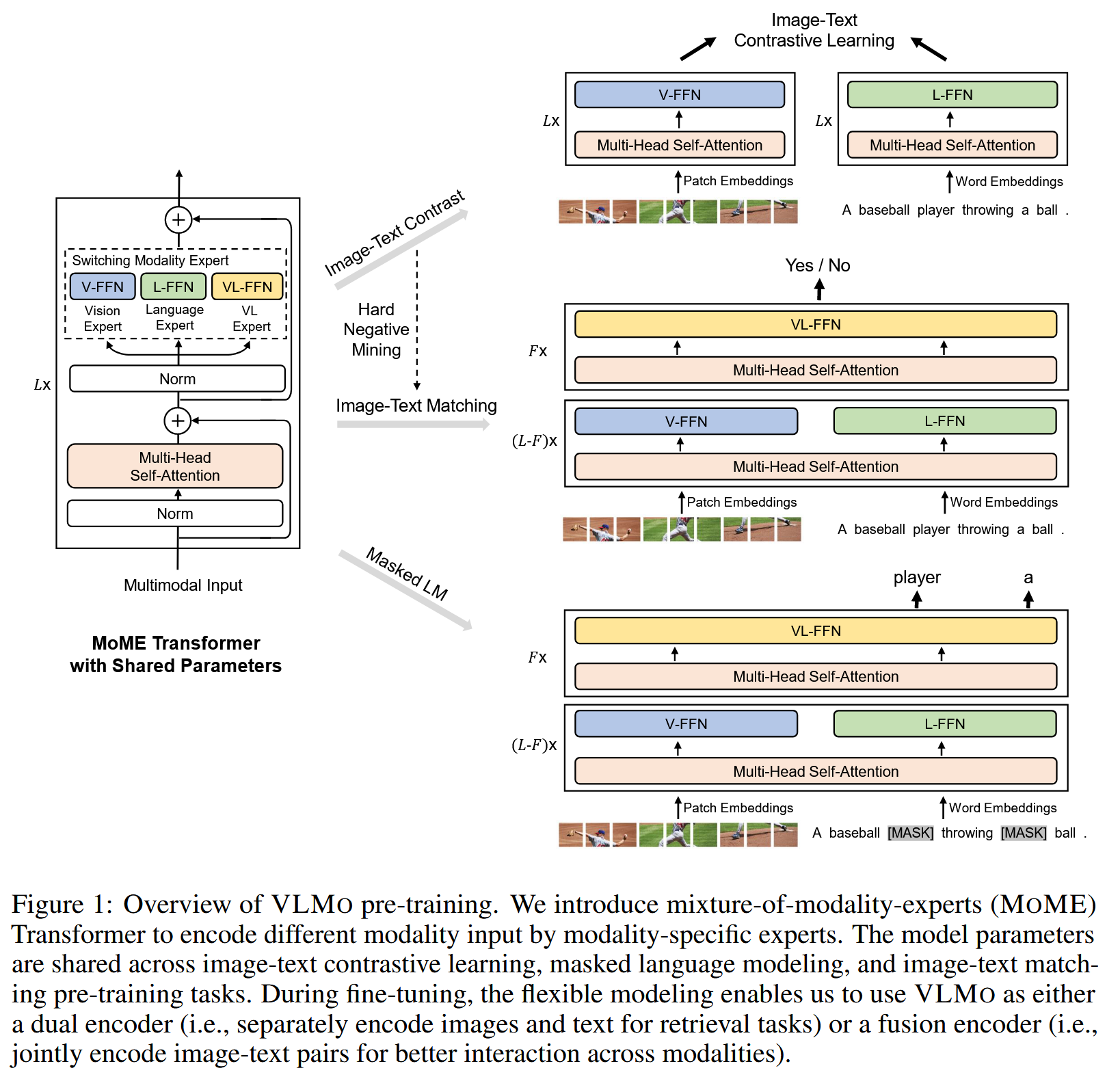
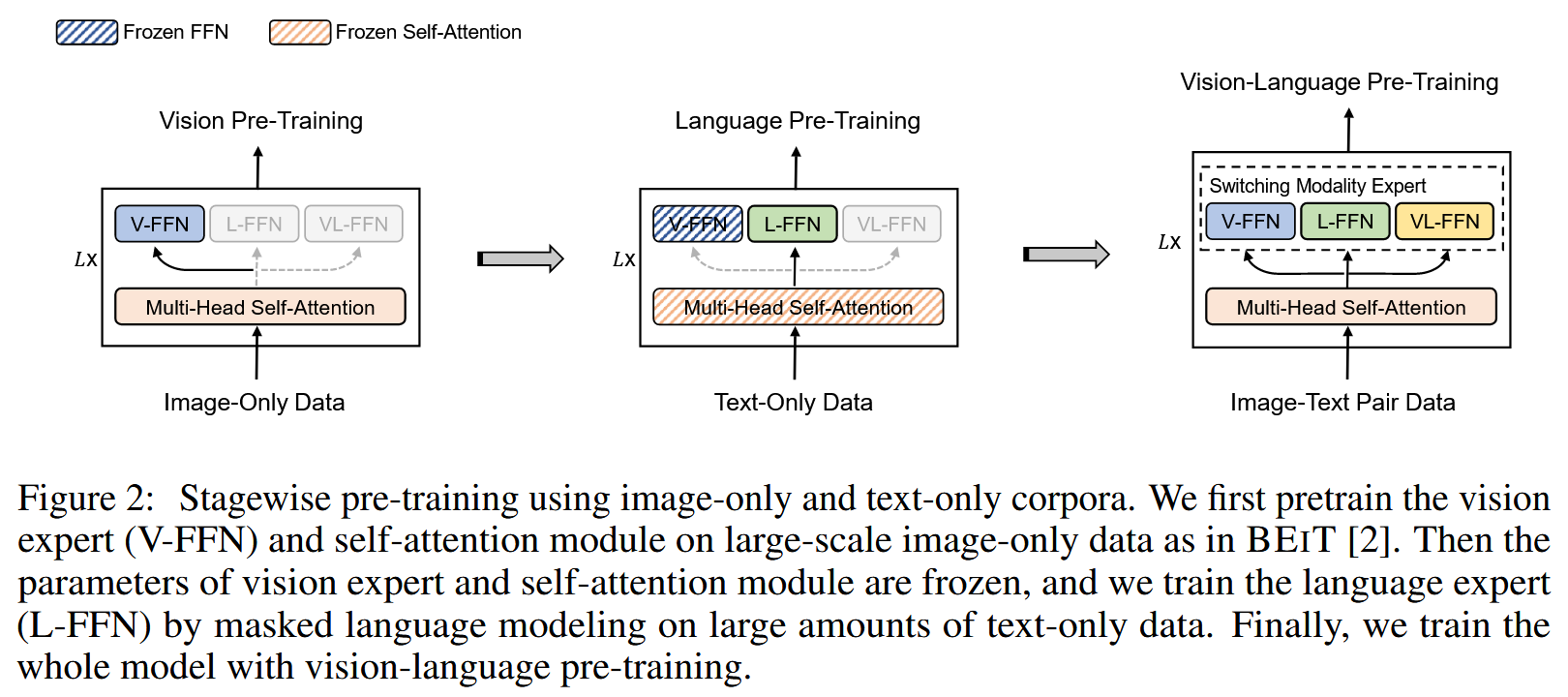
VLMo (2111)
VLMo: Unified Vision-Language Pre-Training with Mixture-of-Modality-Experts
https://arxiv.org/abs/2111.02358
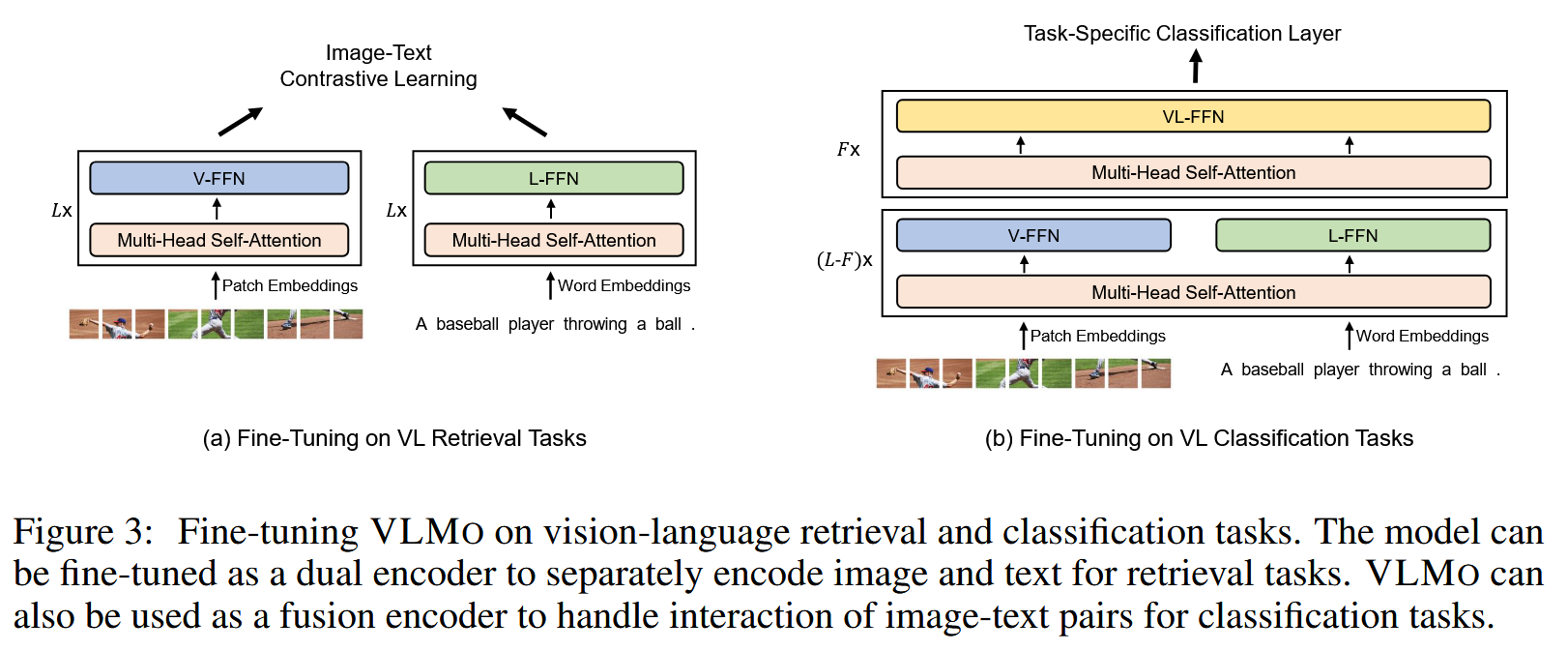
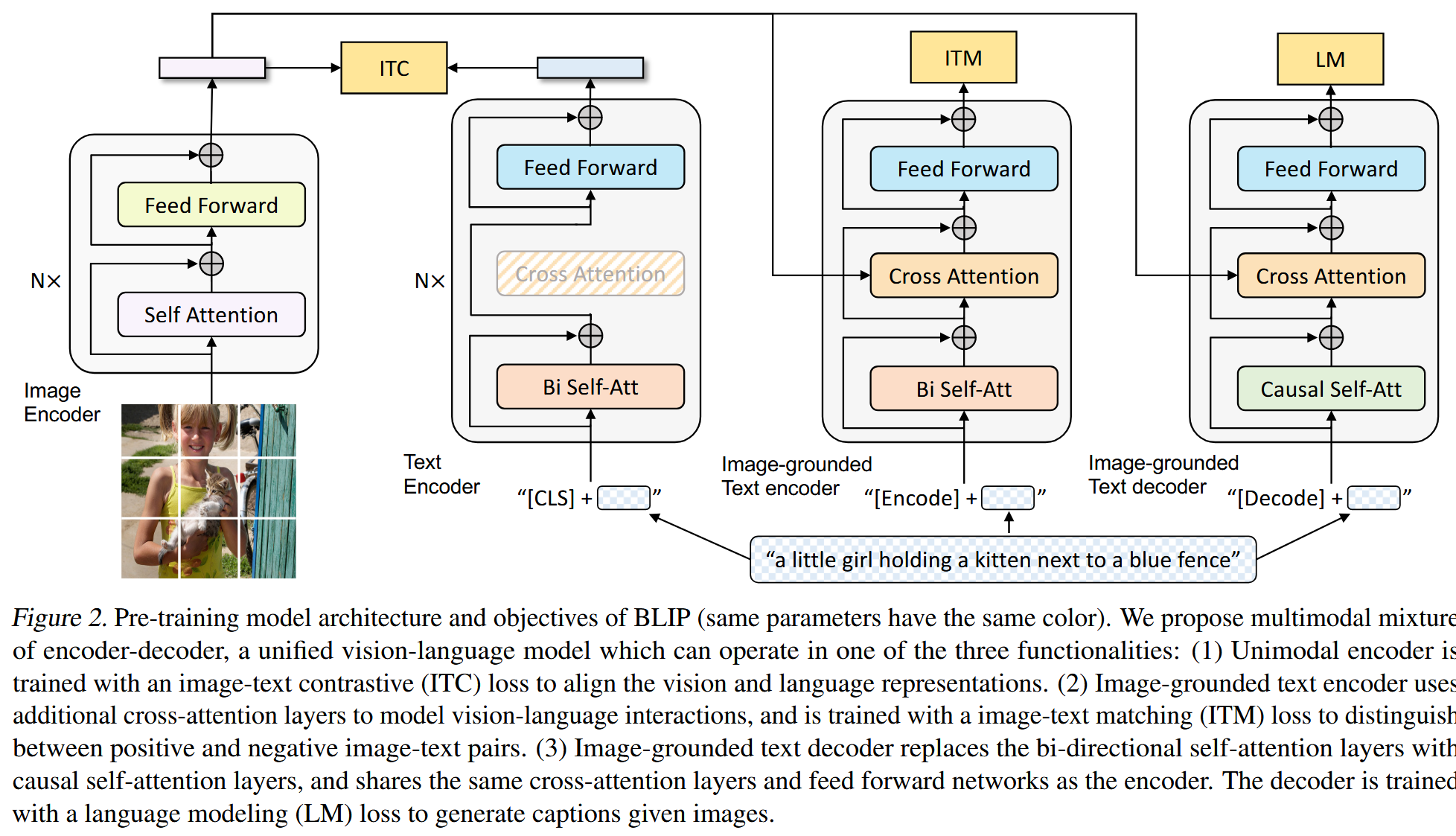
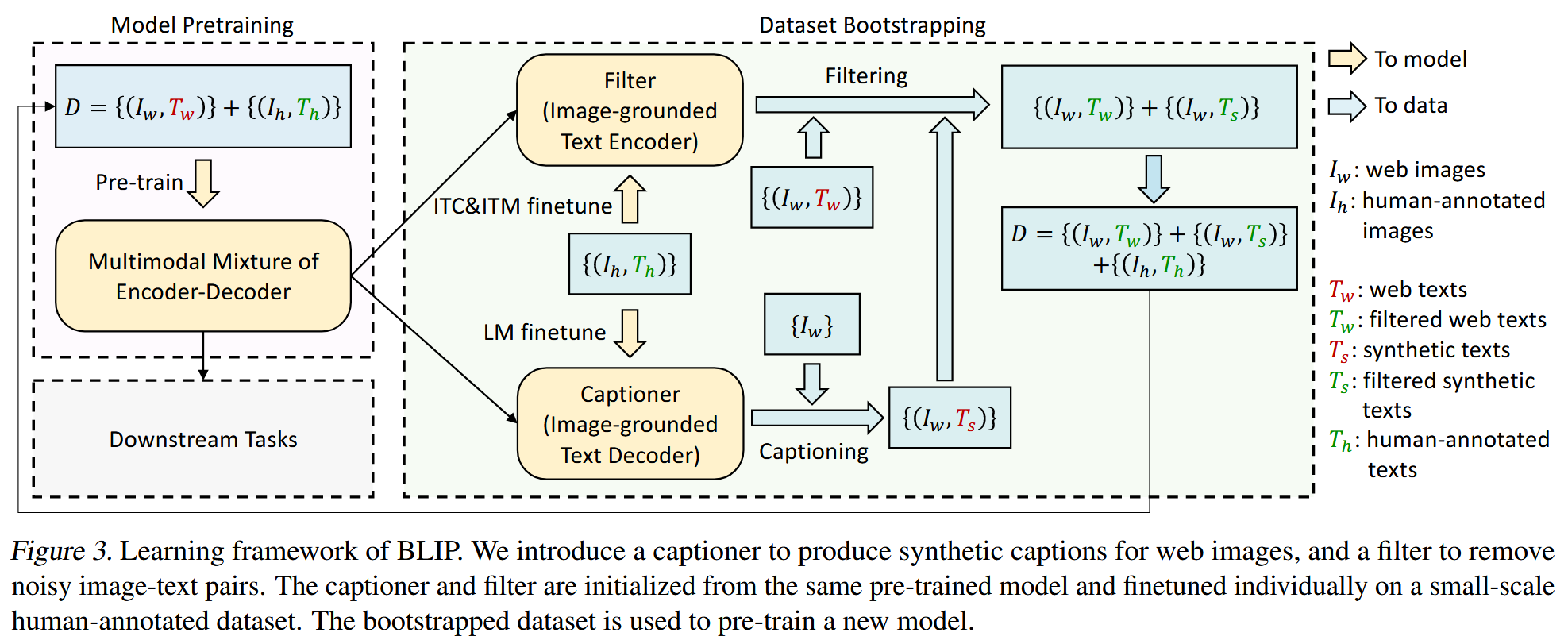
BLIP (2201)
BLIP: Bootstrapping Language-Image Pre-training for Unified Vision-Language Understanding and Generation
https://arxiv.org/abs/2201.12086
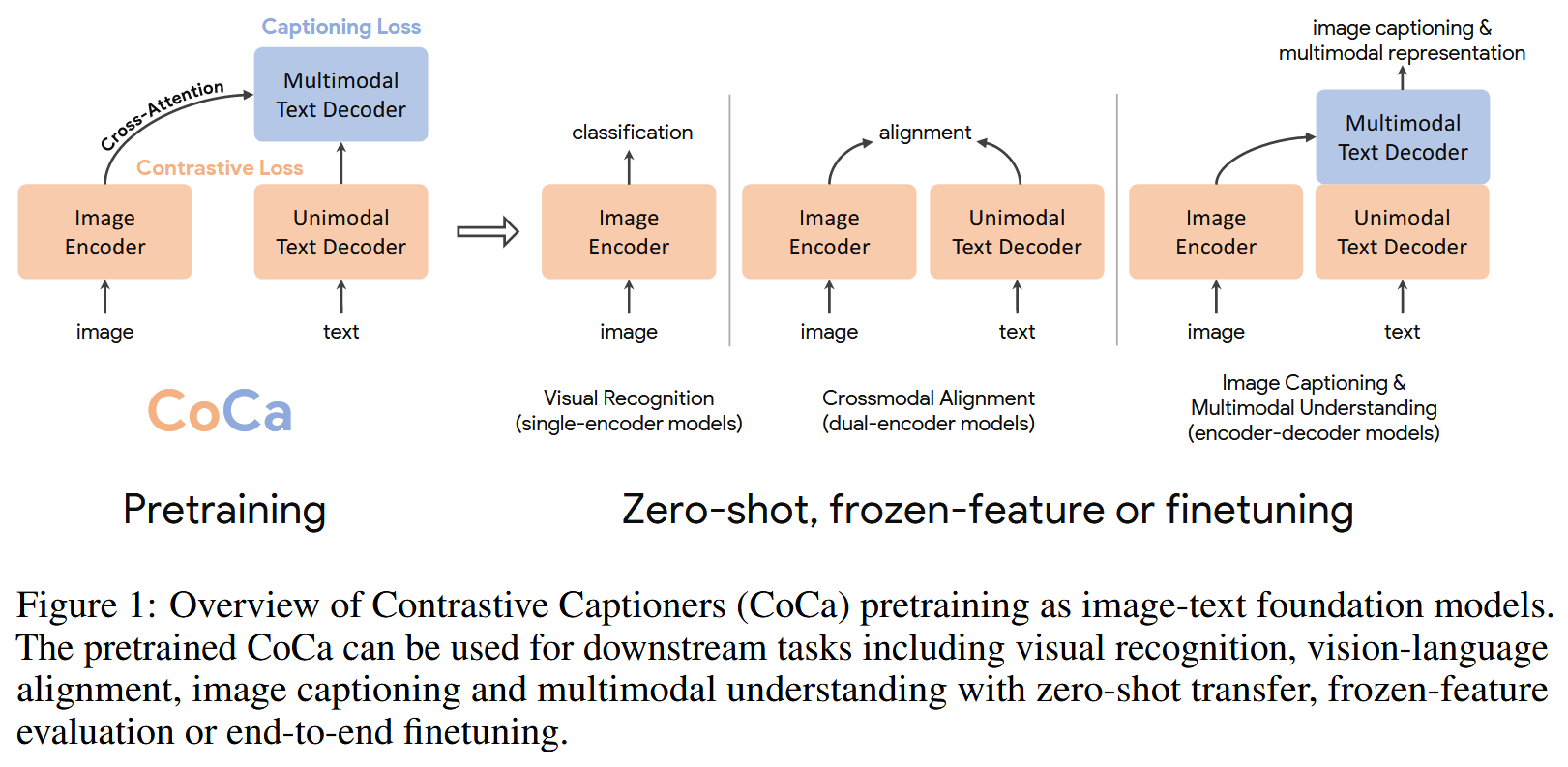
CoCa (2205)
CoCa: Contrastive Captioners are Image-Text Foundation Models
https://arxiv.org/abs/2205.01917
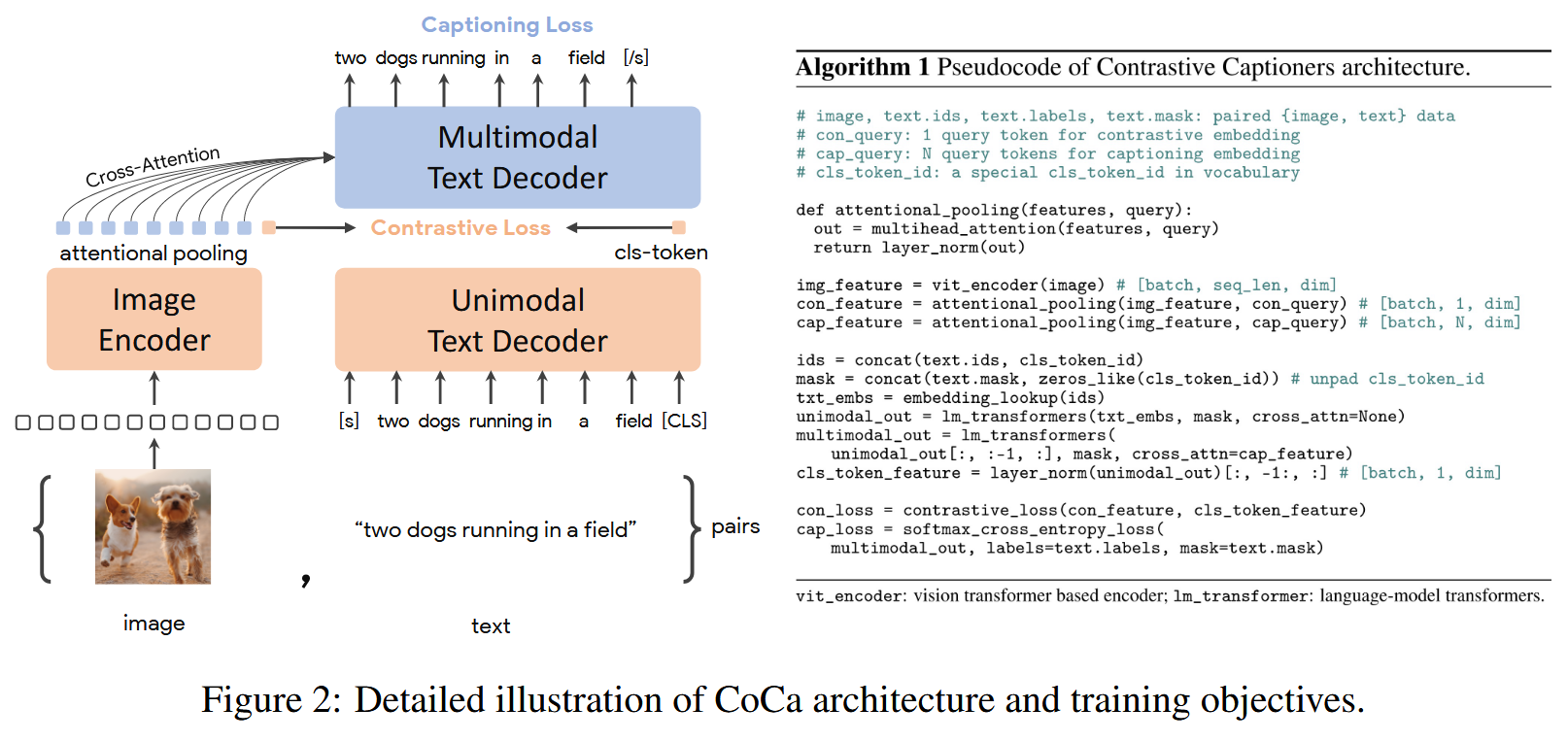
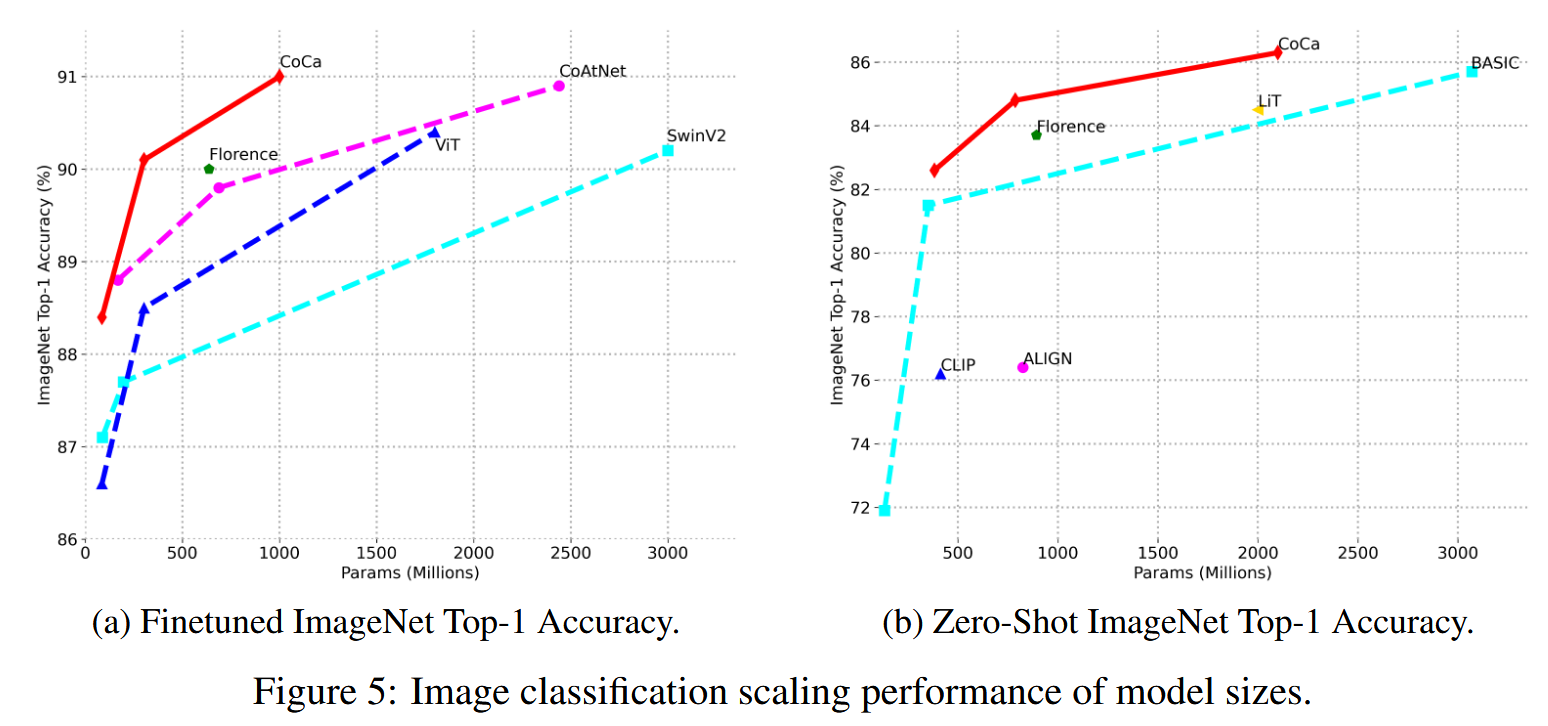
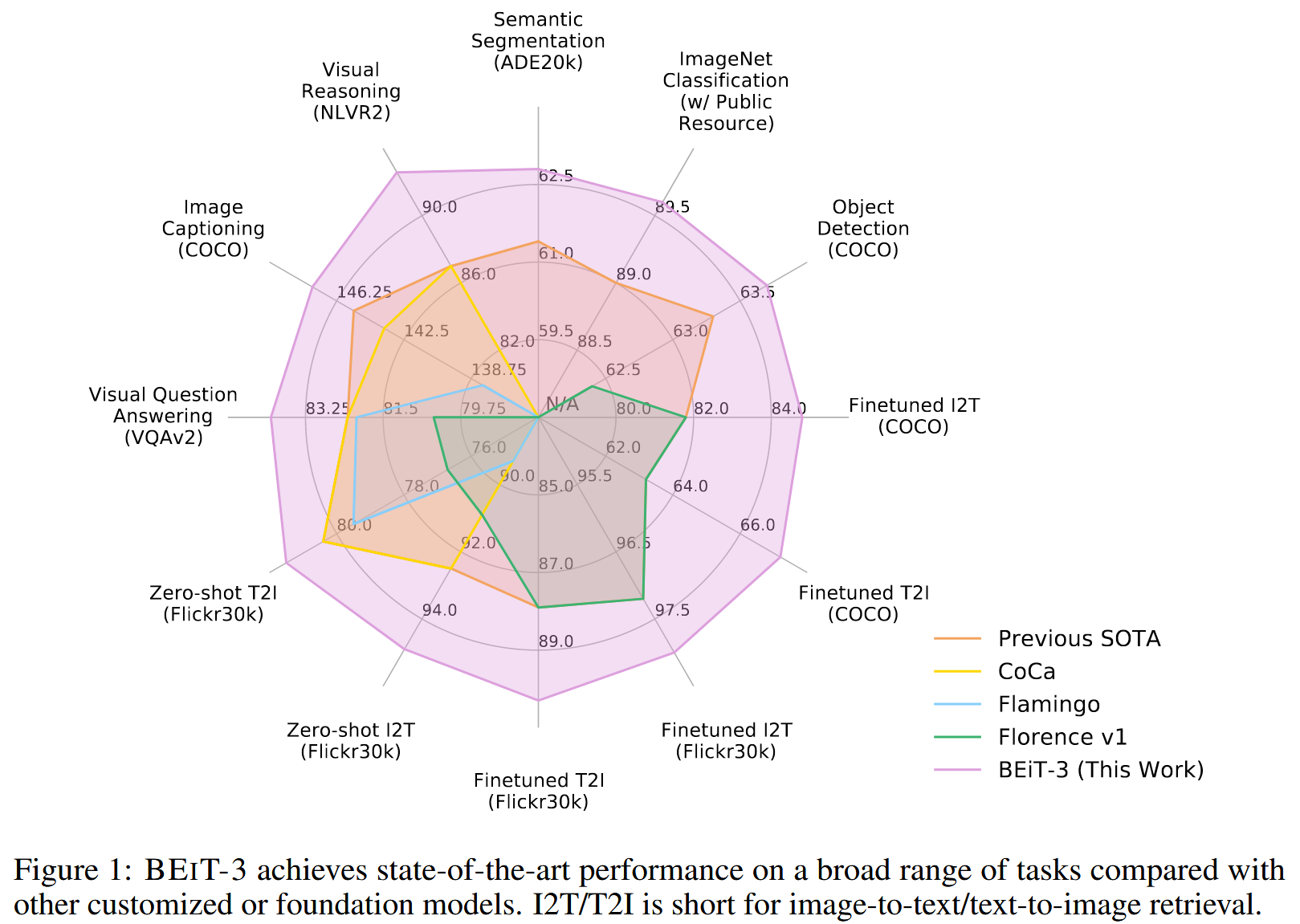
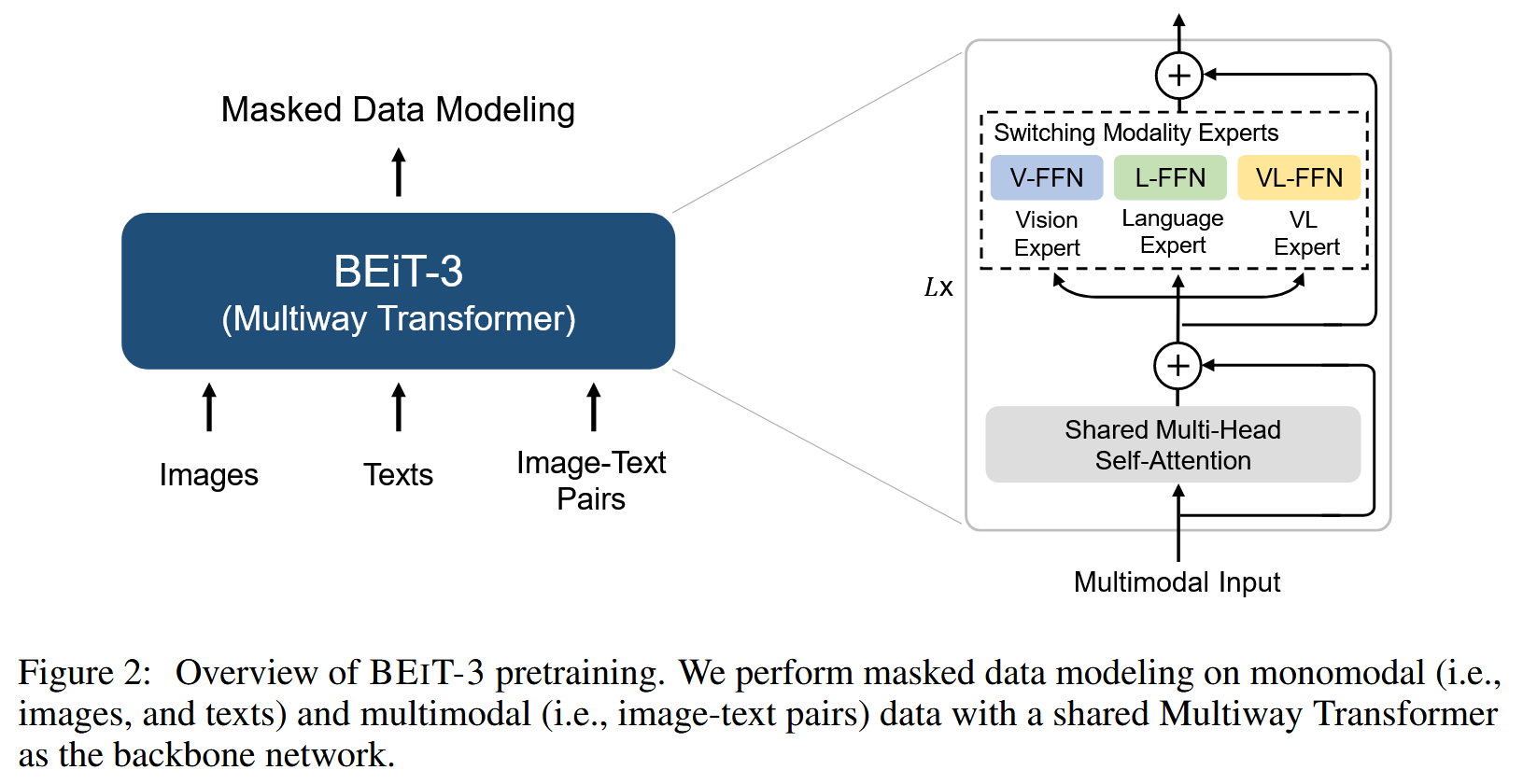
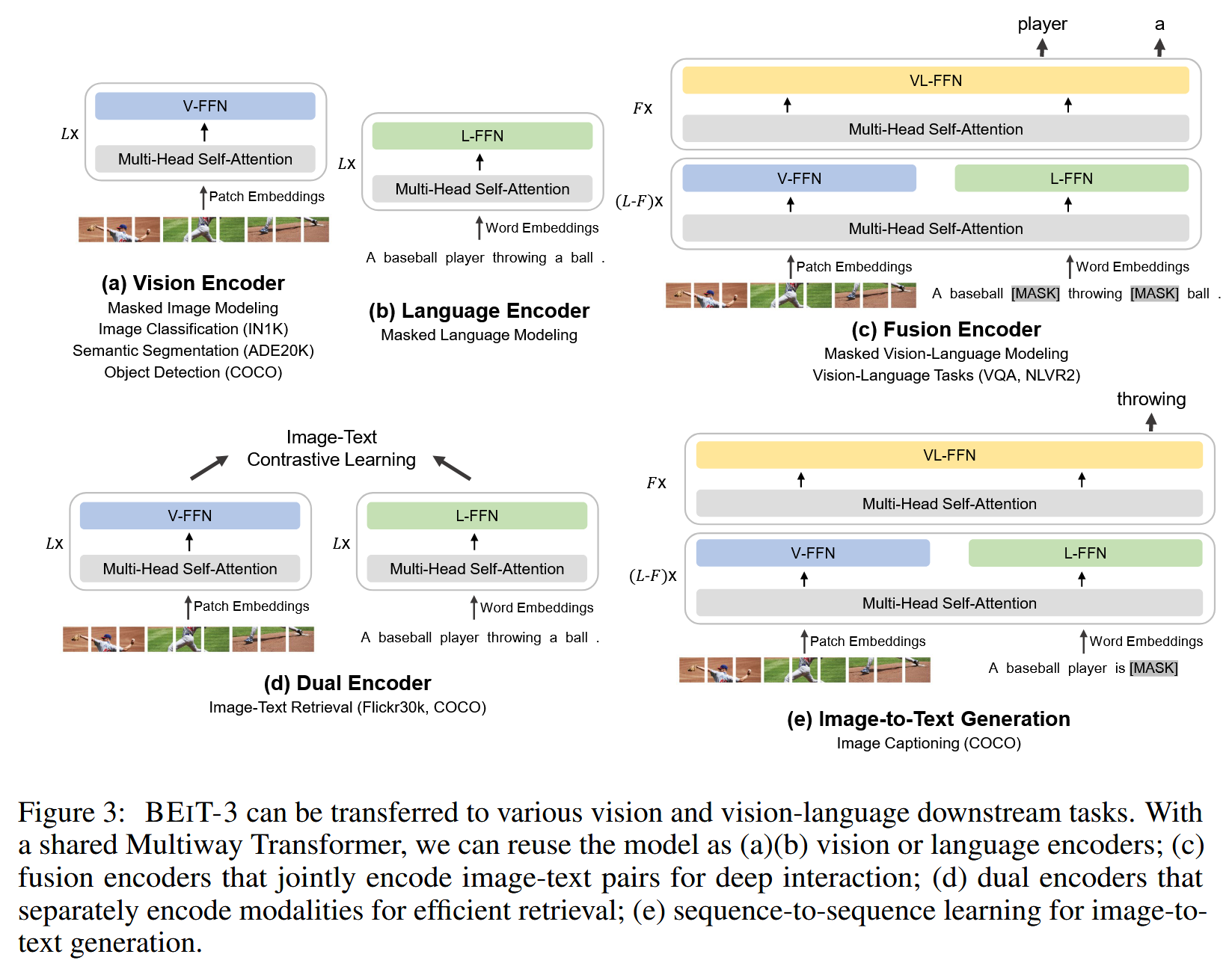
BEiT-3 (2208)
Image as a Foreign Language: BEiT Pretraining for All Vision and Vision-Language Tasks
https://arxiv.org/abs/2208.10442
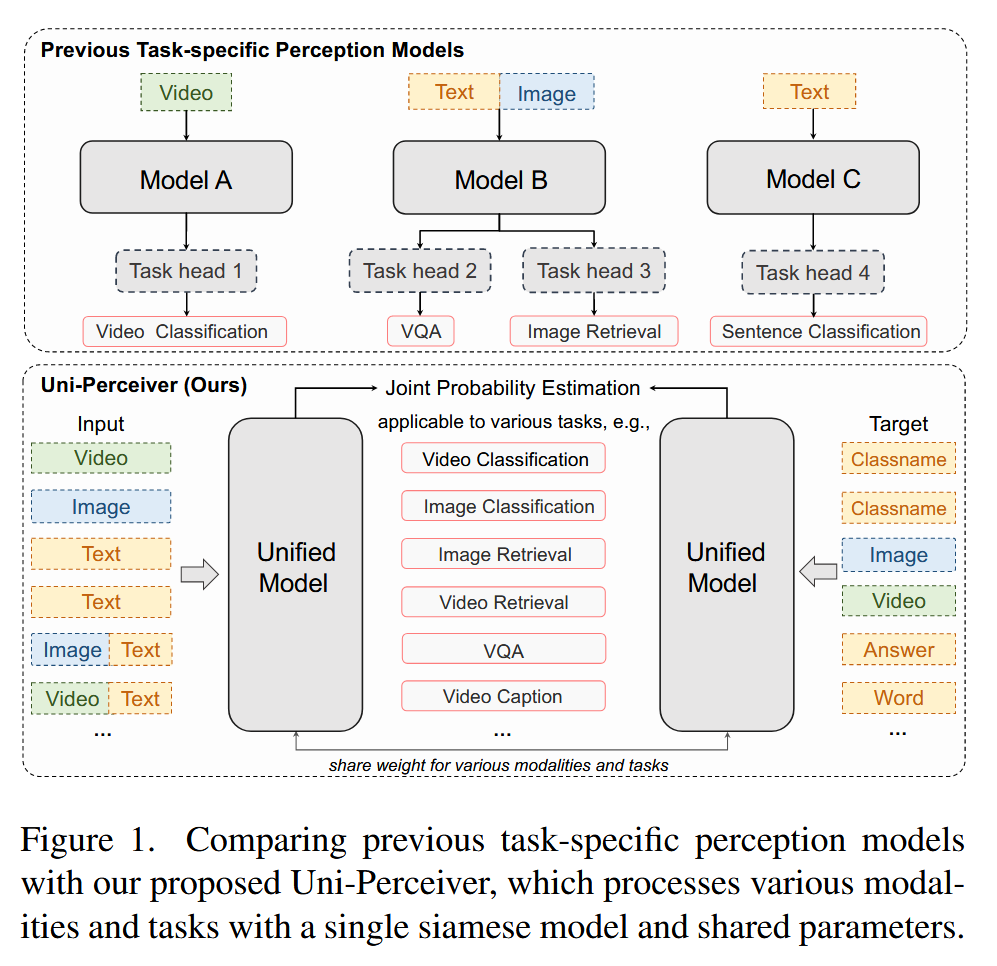
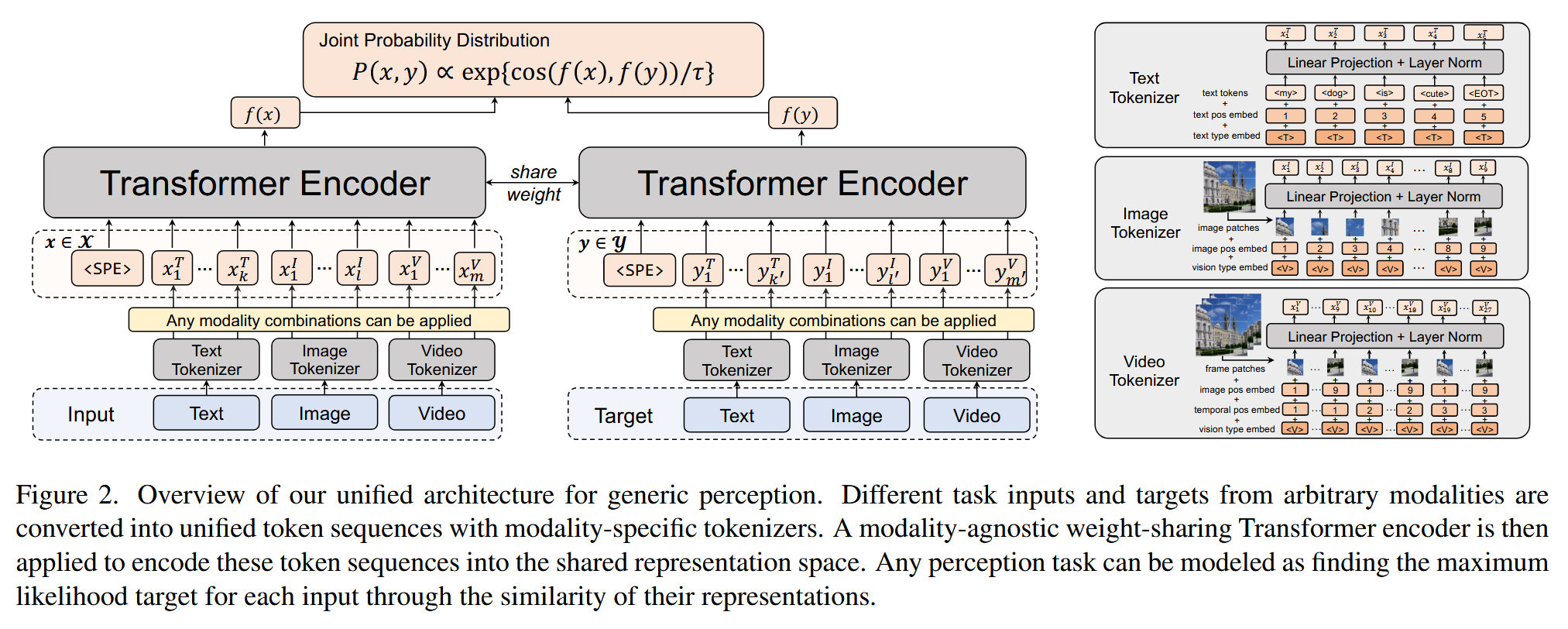
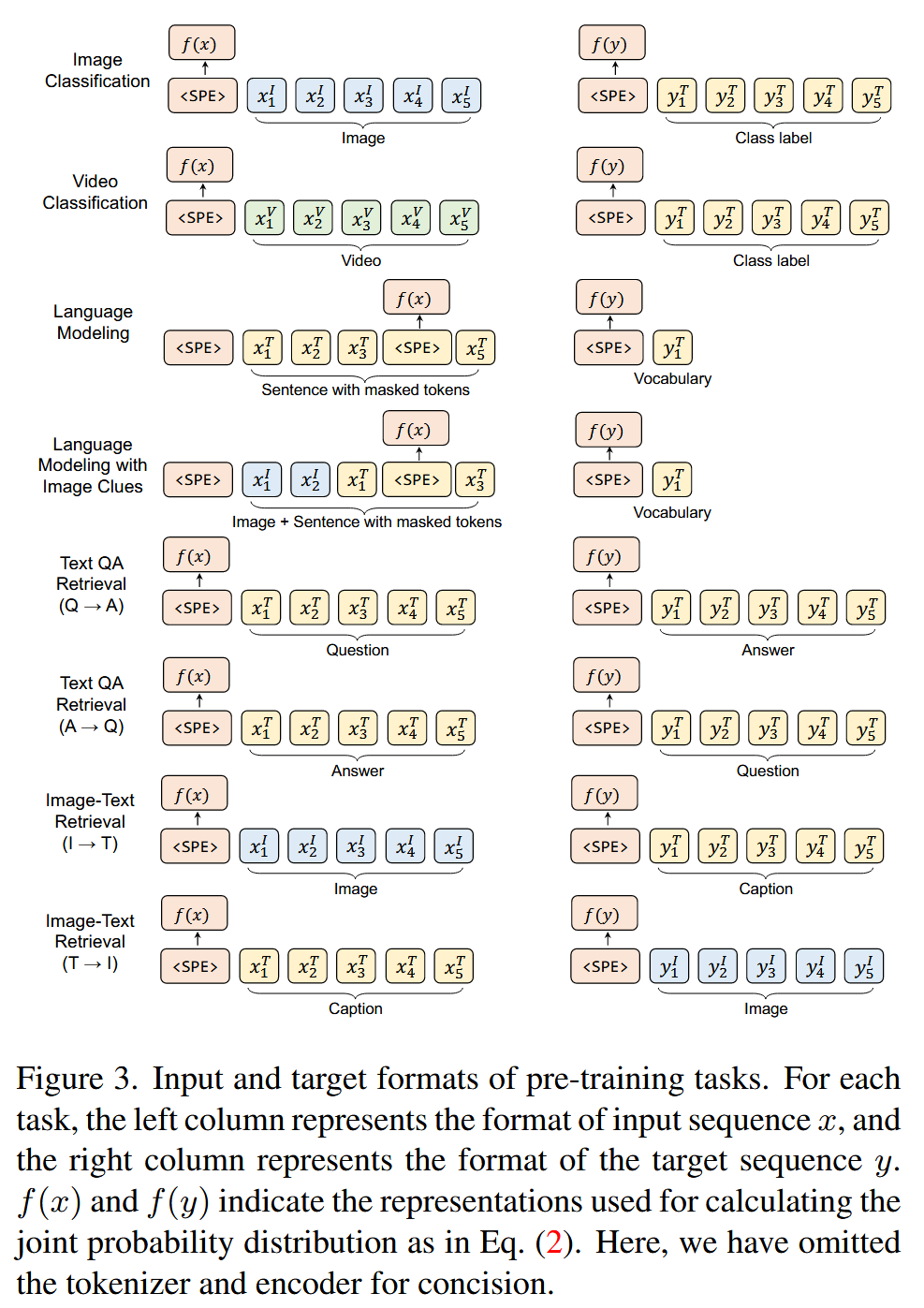
Uni-perceiver系列
Uni-perceiver,Uni-perceiver-moe,Uni-perceiver-v2
Uni-perceiver (2112)
Uni-Perceiver: Pre-training Unified Architecture for Generic Perception for Zero-shot and Few-shot Tasks
https://arxiv.org/abs/2112.01522
PaLI系列
PaLI,PaLI-X,PaLI-v2
多模态大语言模型 | MLLMs
Keywords:
- LMMs(Large Multimodal Models) | 大多模态模型
- MLLMs(Multimodal Large Language Models) | 多模态大语言模型
Survey
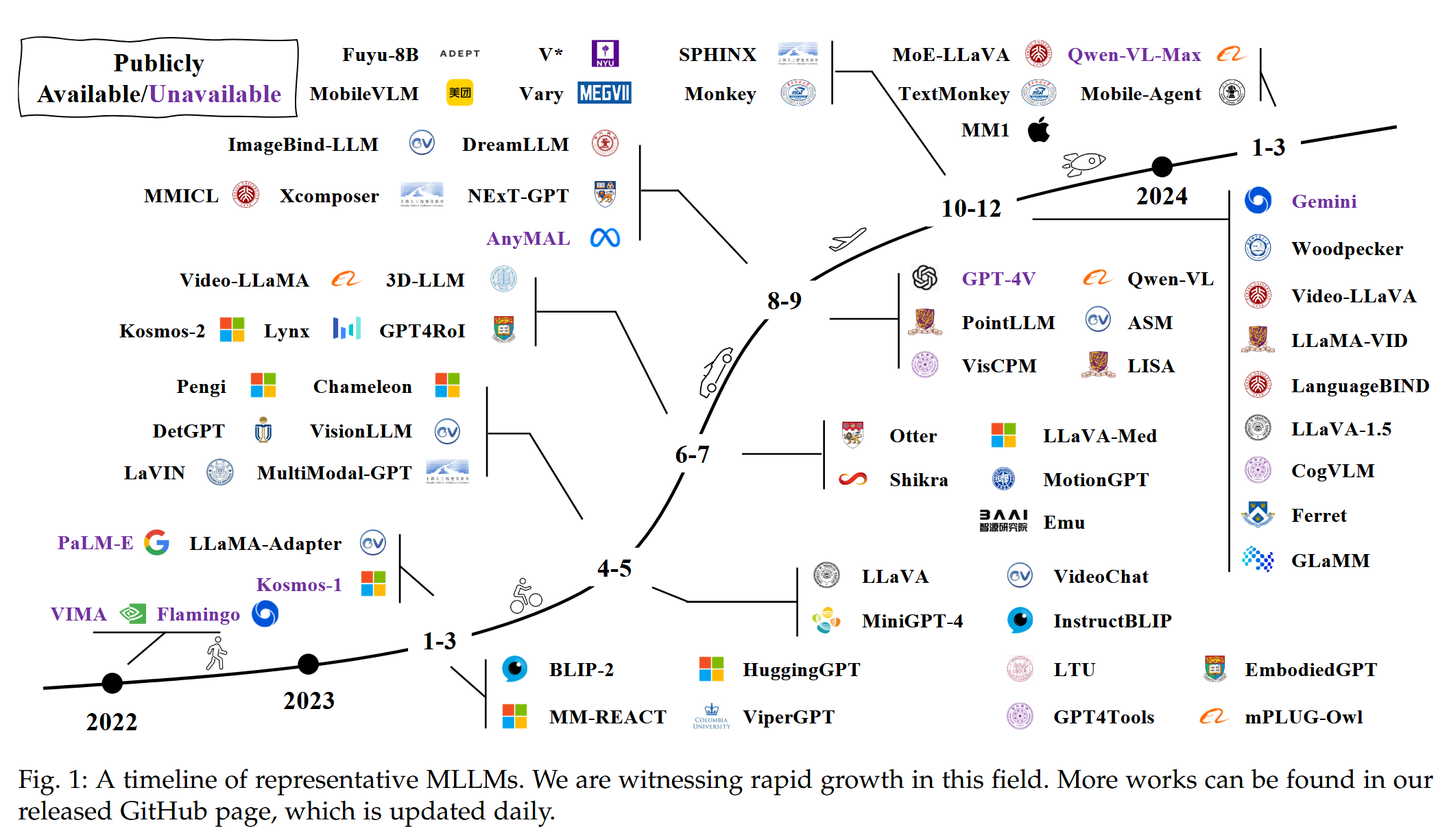
MM-LLMs (2024.05)
MM-LLMs: Recent Advances in MultiModal Large Language Models
- arXiv:2401.13601v5 [cs.CL] 28 May 2024
- https://arxiv.org/pdf/2401.13601
- web: https://mm-llms.github.io/ ⭐
- Recent Advances in MLLMs

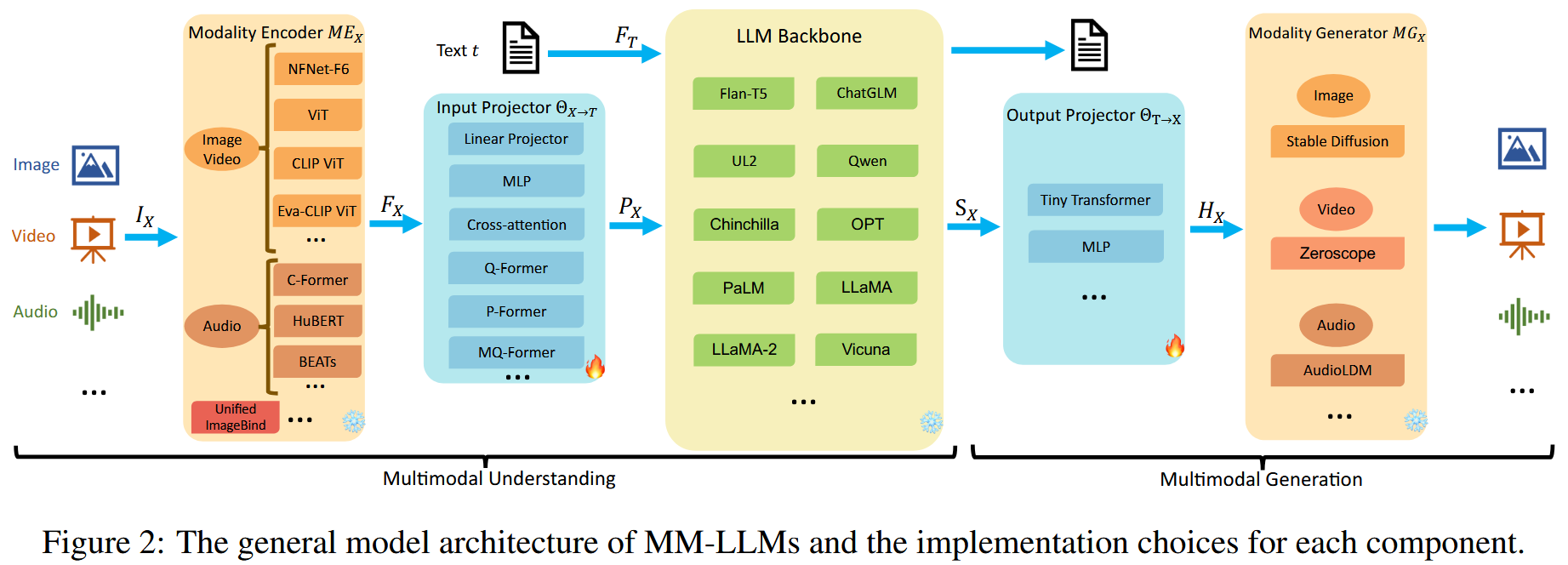
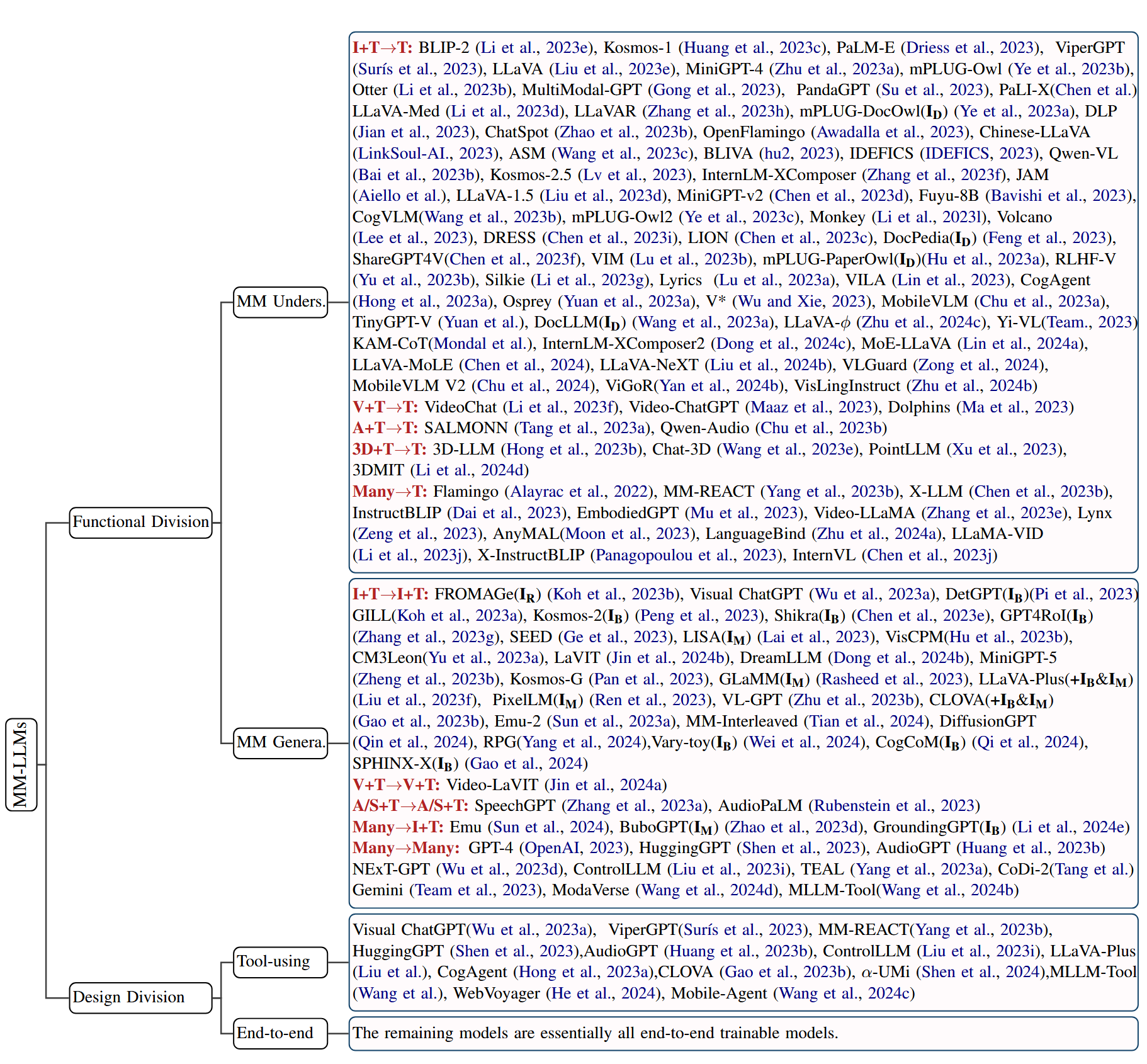
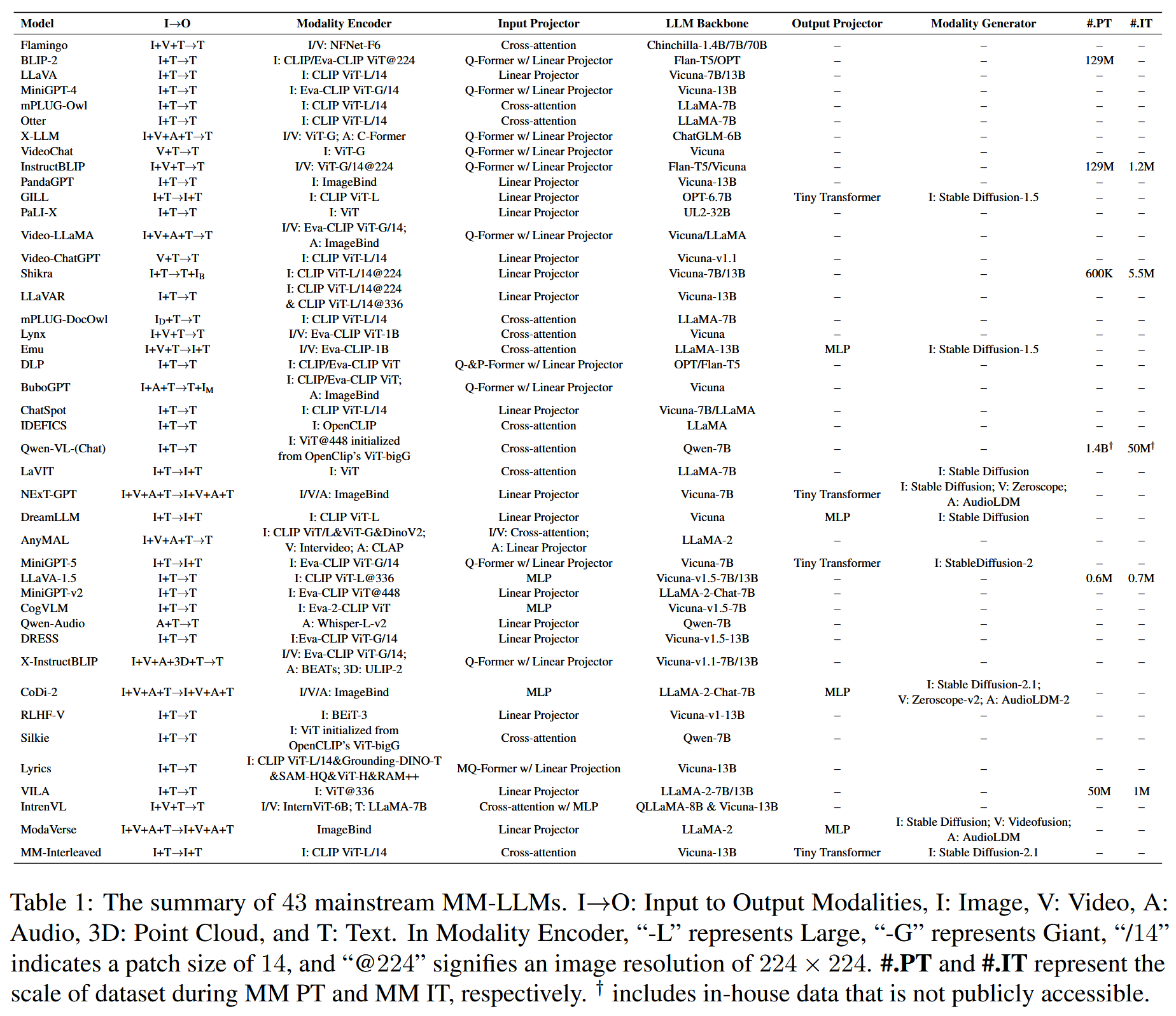
A Survey on MLLMs (2024.11)
A Survey on Multimodal Large Language Models
- arXiv:2306.13549v4 [cs.CV] 29 Nov 2024
- https://arxiv.org/abs/2306.13549
- The first comprehensive survey for Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs). ✨
- code: https://github.com/BradyFU/Awesome-Multimodal-Large-Language-Models


MME-Survey (2024.12)
MME-Survey: A Comprehensive Survey on Evaluation of Multimodal LLMs
- arXiv:2411.15296v2 [cs.CV] 8 Dec 2024
- https://arxiv.org/abs/2411.15296
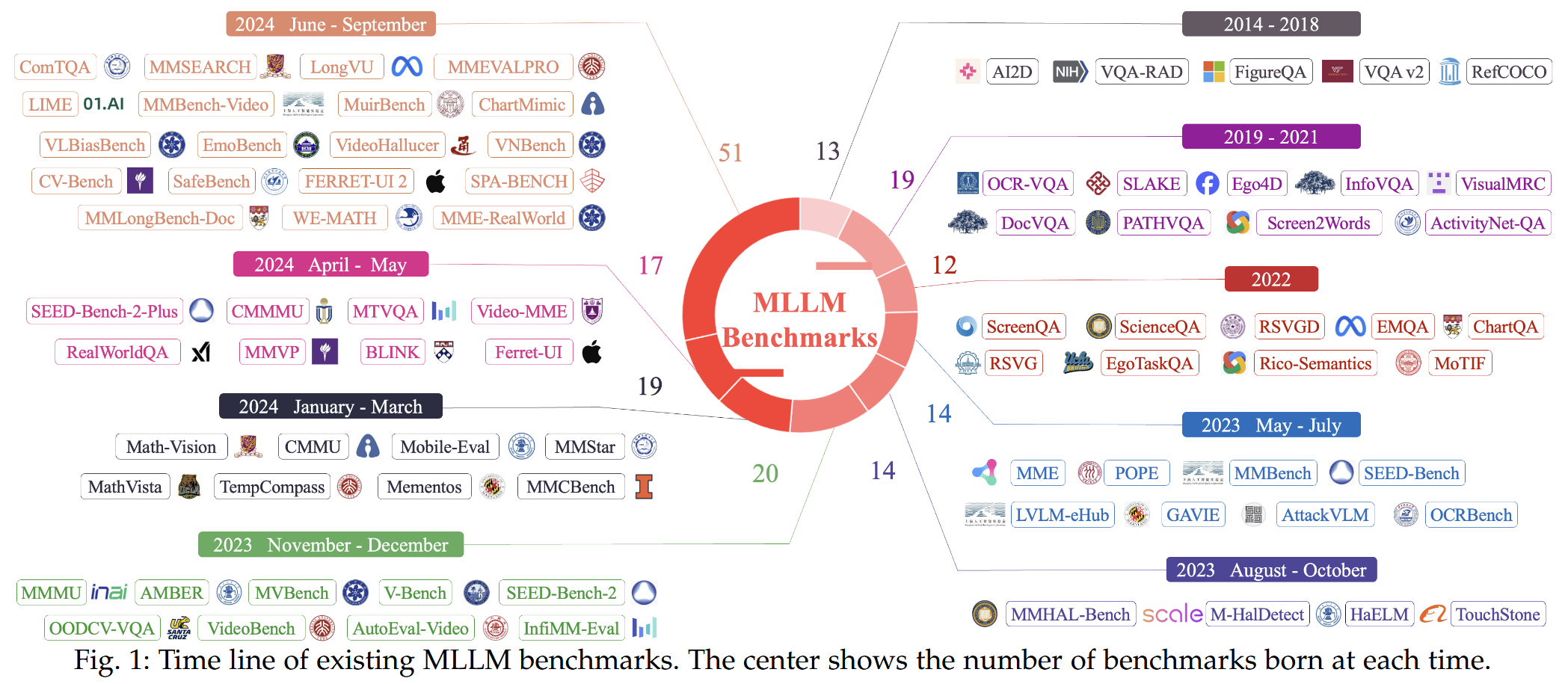
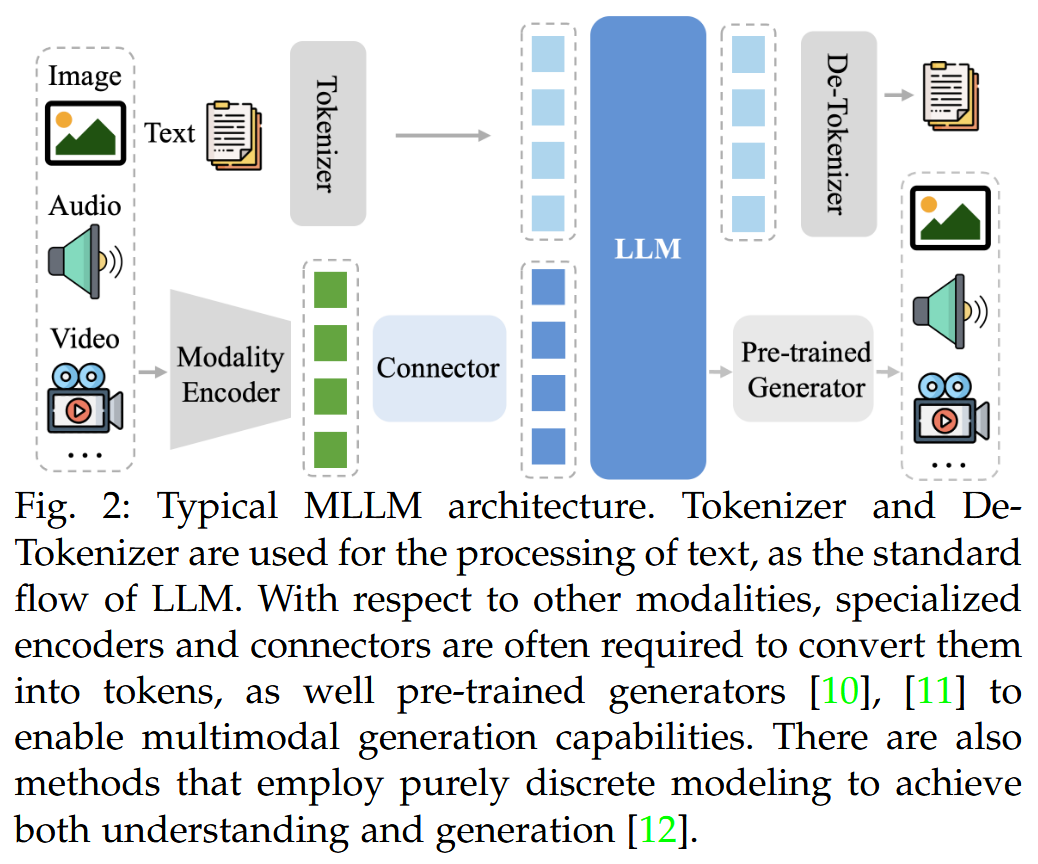
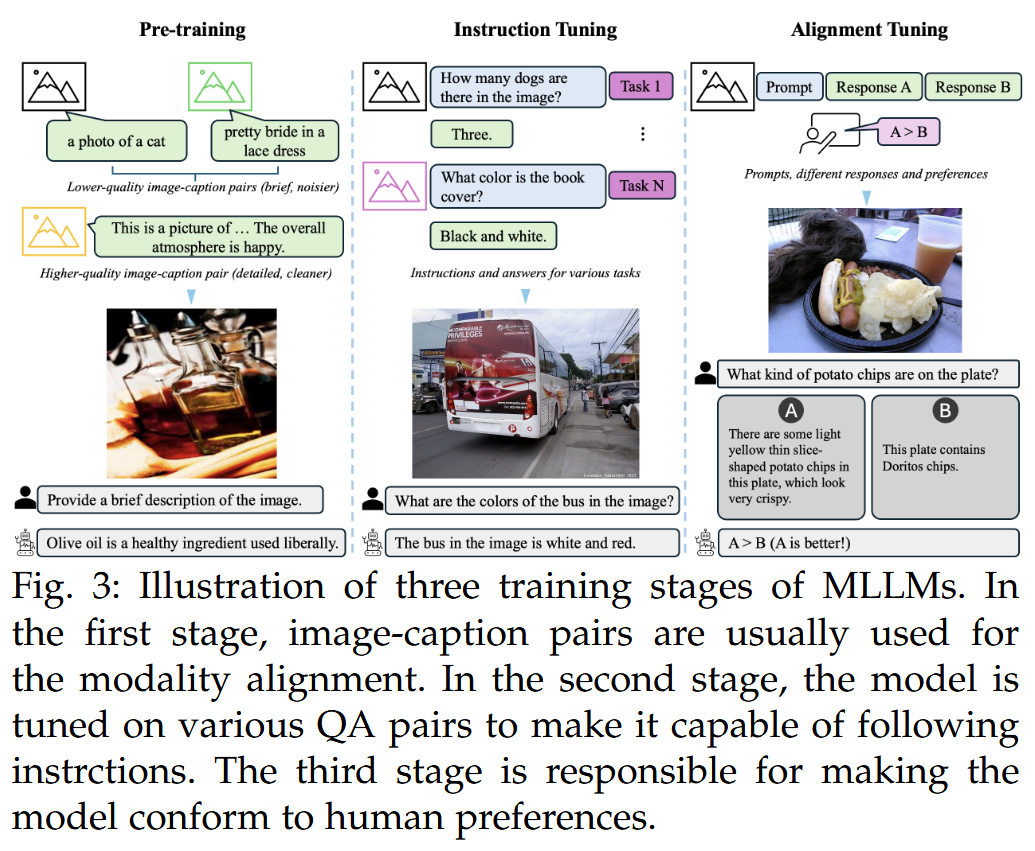
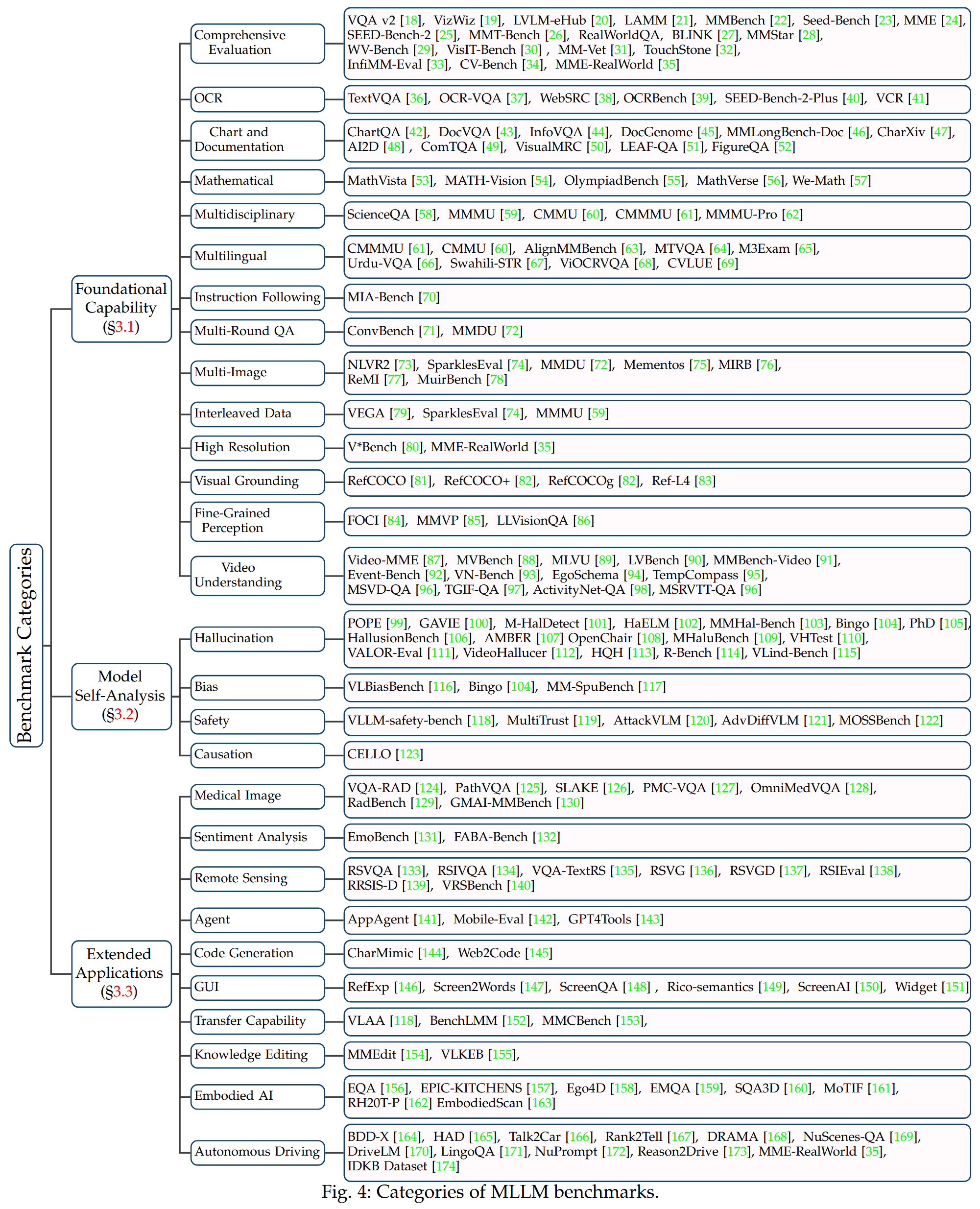
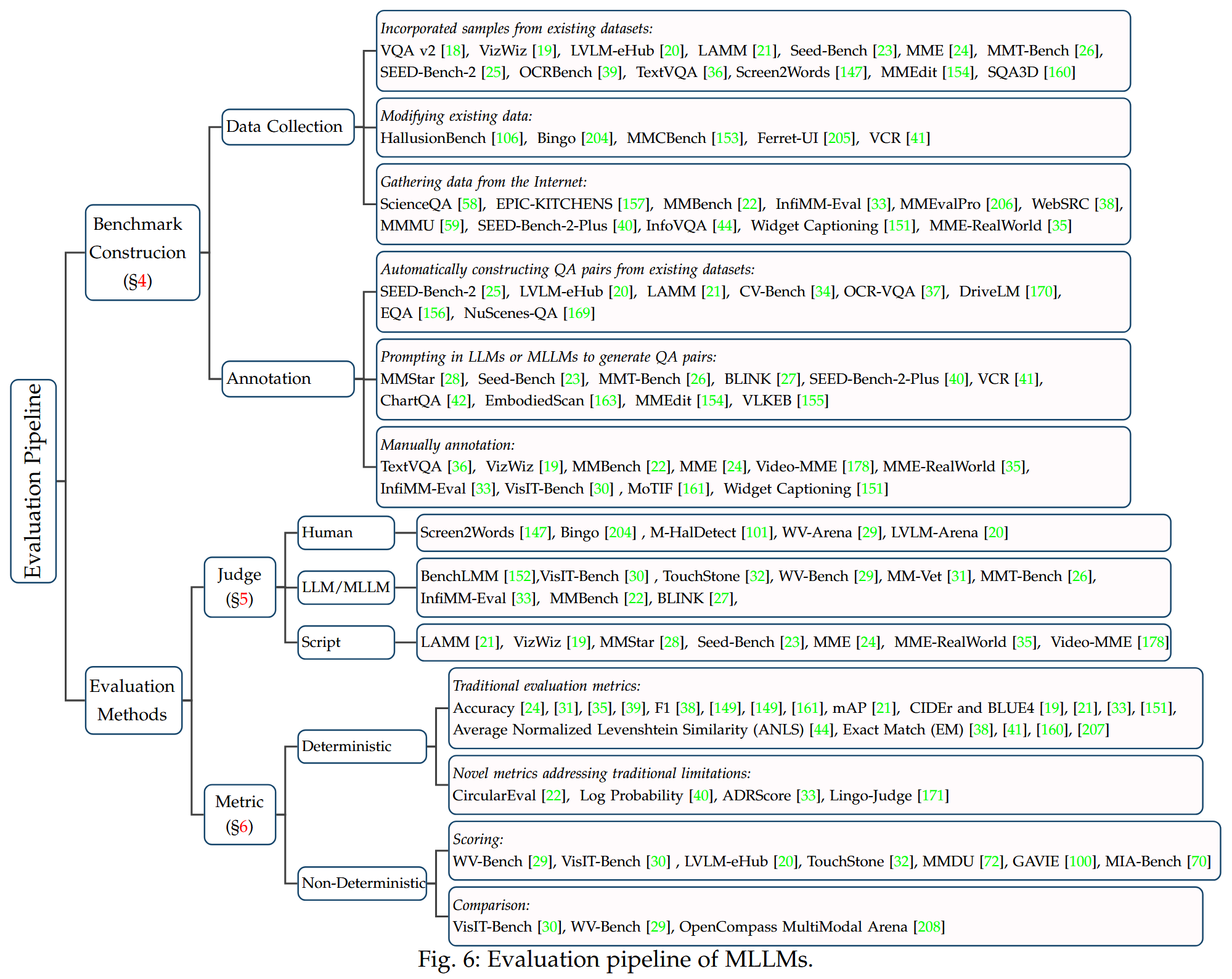
Models
LLaVA系列
- blog: https://llava-vl.github.io/
- github: https://github.com/haotian-liu/LLaVA
- datasets: liuhaotian/LLaVA-Instruct-150K
LLaVA [NeurIPS’23]
paper: Visual Instruction Tuning
- arXiv:2304.08485v2 [cs.CV] 11 Dec 2023
- NeurIPS’23 Oral
- 核心Idea:
- 此前的 LLMs 通过 Instruction Tuning(指令调优)提高了zero-shot能力
- 我们提出
Visual Instruction Tuning (视觉指令调优)来提高LMMs的zero-shot能力
- Performance:主要对标 GPT-4(闭源),超越 OpenFlamingo(开源)和 BLIP-2(开源)
- LLaVA+GPT-4(judge) 当时在多模态推理数据集 ScienceQA 上实现 new SOTA (92.53)
- 模型大小:13B(default), 7B
- 训练成本:仅用单机8张A100,训练不到一天
Related Work
Multimodal Instruction-following Agents
- 第1类:端到端模型。如 vision-language navigation task, Habitat(具身智能);InstructPix2Pix(图像编辑)
- 第2类:多模型协作(通过LangChain)。如 Visual ChatGPT, X-GPT, MM-REACT, VisProg, ViperGPT
Instruction Tuning
- LLMs:GPT-3, T5, PaLM, OPT
- 指令微调(简单方法提高zero-shot/few-shot能力):INstructGPT/ChatGPT, FLAN-T5, FLAN-PaLM, OPT-IML
- LMMs:BLIP-2, FROMAGe, KOSMOS-1, PaLM-E; Flamingo (因其强大的zero-shot迁移能力和In-Context-Learning能力,可以被视为多模态领域的GPT-3 moment)
- OpenFlamingo, LLaMA-Adapter 让 recent “best” open-source LLM LLaMA 能接收image输入(但他们没有显式的在vision-language instruction data上微调,并且在多模态任务上通常表现下降)
- LLMs:GPT-3, T5, PaLM, OPT
Contributions
- 【合成数据】 Multimodal language-image instruction-following data
- 一个重要挑战是缺乏vision-language instruction-folling data,我们提出第一个使用
language-only ChatGPT/GPT4,从image-text pairs构造训练数据 的pipeline
- 一个重要挑战是缺乏vision-language instruction-folling data,我们提出第一个使用
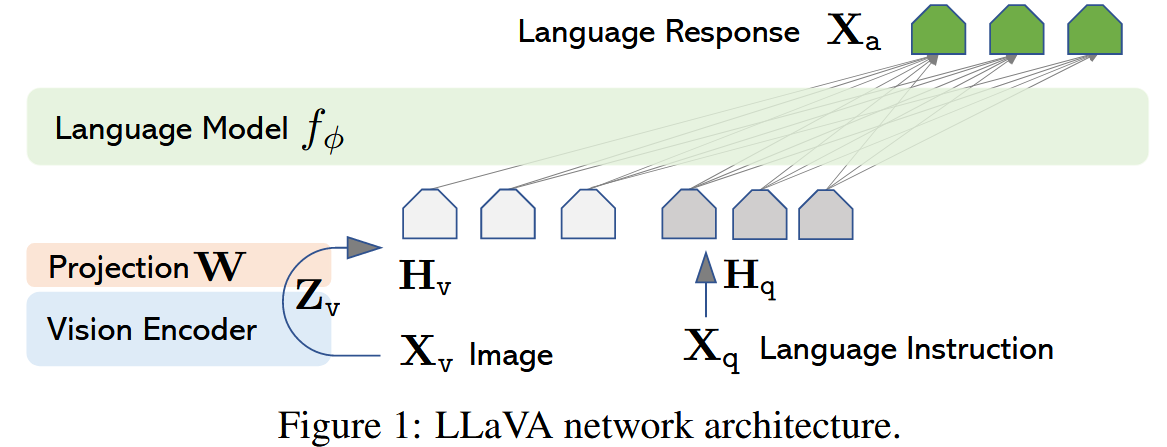
- 【模型架构】 Large Multimodal Models(LMMs)

- pretrained
Visual Encoder- 架构:CLIP visual encoder ViT-L/14
- 功能:提取 input image
的视觉特征得到 visual features - 视觉特征:the grid features before/after the last Transformer layer
- features before last layer: 更关注 localized properties,有助于模型理解specific image details ⭐(效果更好)
- features after last layer: 更关注 global and abstract image properties
projection layer- 架构:一个简单的线性层 ⭐(将来也可以考虑尝试gated cross-attention in Flamingo 或者 Q-former in BLIP-2)
- 功能:映射 visual features
到LLM的word embedding space中得到 visual tokens - 备注:后续LLaVA-1.5中叫做
Vision-Language Connector
- pretrained
Language Decoder (LLM)- 架构:Vicuna (小羊驼,在语言任务上的instrction following能力是当时开源模型中最好的)
- 功能:提供 instruction following 和 reasoning 能力
- pretrained
- 【新的基准】 Multimodal instruction
- 我们提出
LLaVA-Bench (COCO)和LLaVA-Bench (In-the-Wild)作为第一个量化评估LMMs的 visual instruciton following 能力 的benchmark
- 我们提出
- 【全开源】 Open-source
- the generated data
- the model checkpoints
- a visual chat demo
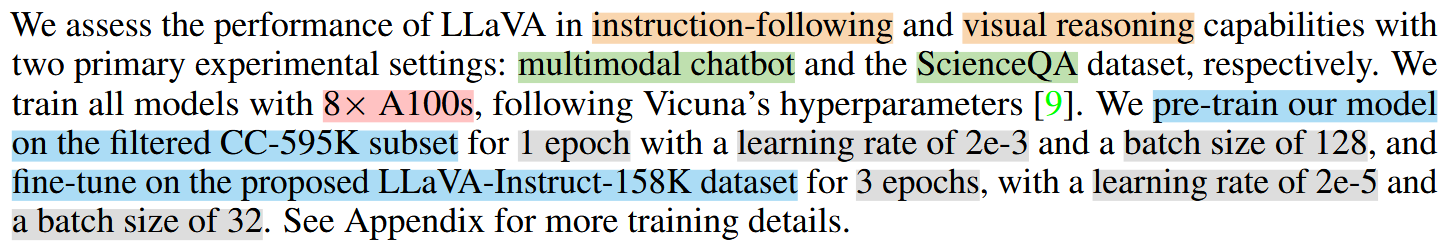
Model Training (two-stage)
(Visual Encoder一直是冻结的)
Stage 1: Pre-training for Feature Alignment
冻结Visual Encoder和LLM,仅训练 projection layer -> 使Visual Encoder兼容LLM,从而visual tokens能对齐pretrained LLM的词向量
Stage 2: Fine-tuning End-to-End
更新 the pre-trained weight of the projection layer and LLM
Experiment
1.Multimodal Chatbot
定性评估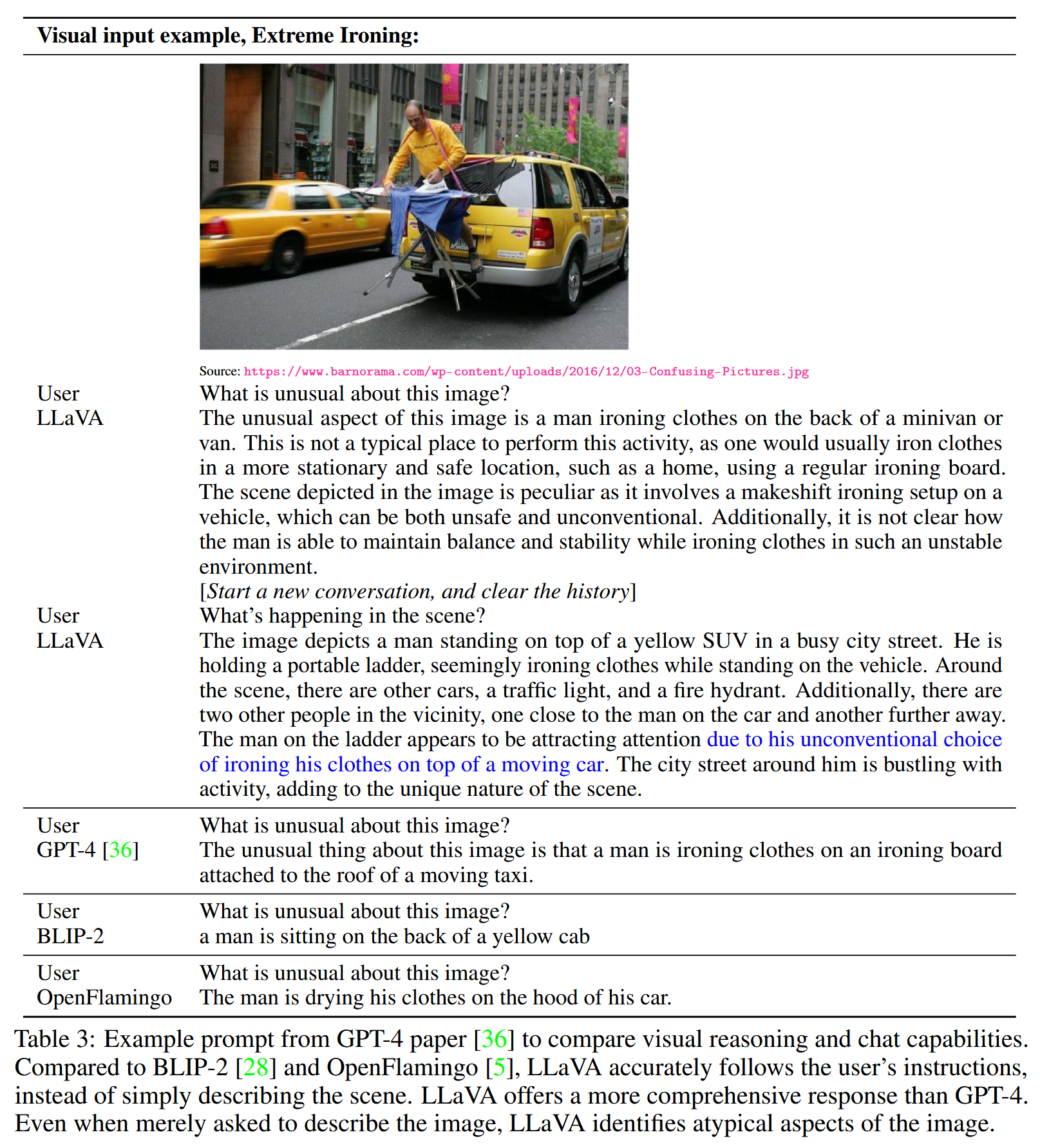
定量评估(在LLaVA-Bench上)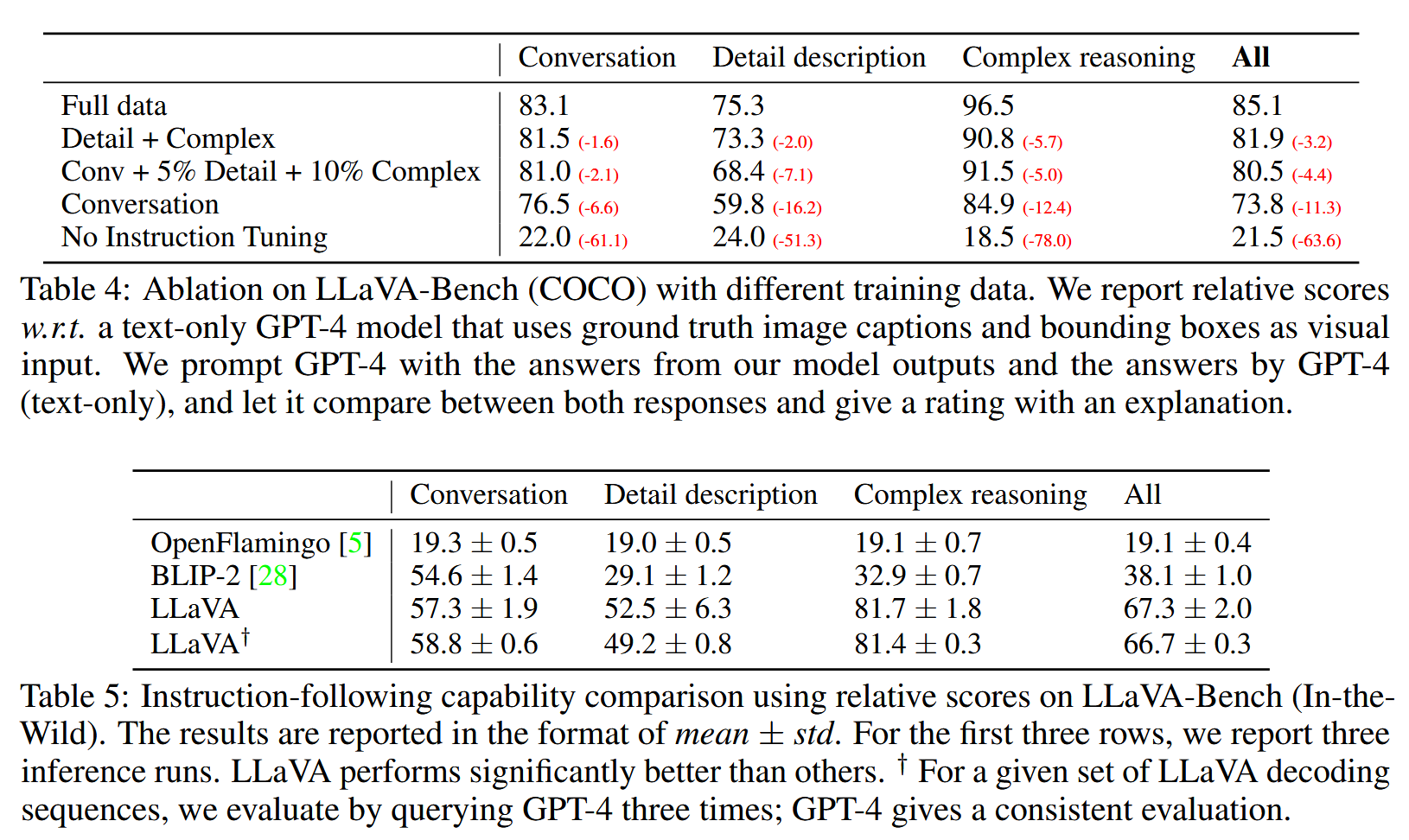
2.SinceQA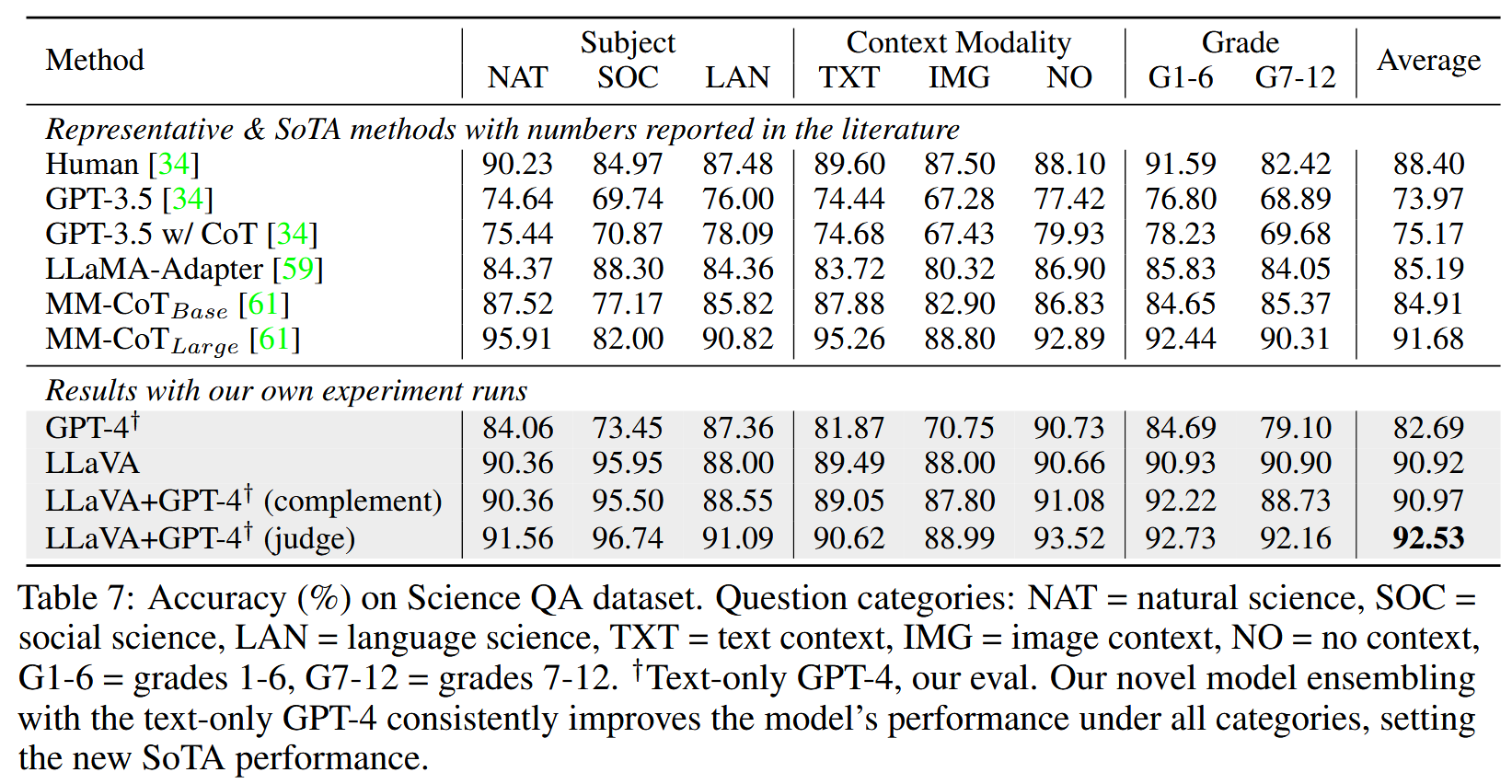
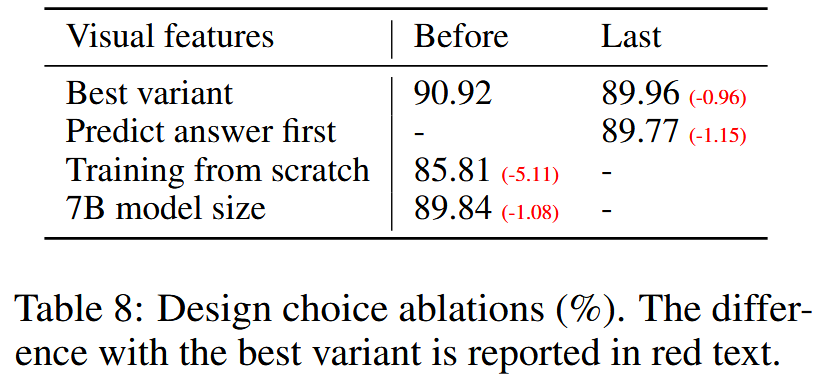
Ablation
- 视觉特征:feature before last layer(关注局部特征) > feature after last year(关注全局和抽象特征)
- 思维链(Chain-of-Thought): answer-first(收敛慢,效果好) > reasoning-first(收敛快,效果差)
- 预训练:有pre-training > 无pre-training
- 模型大小:13B > 7B
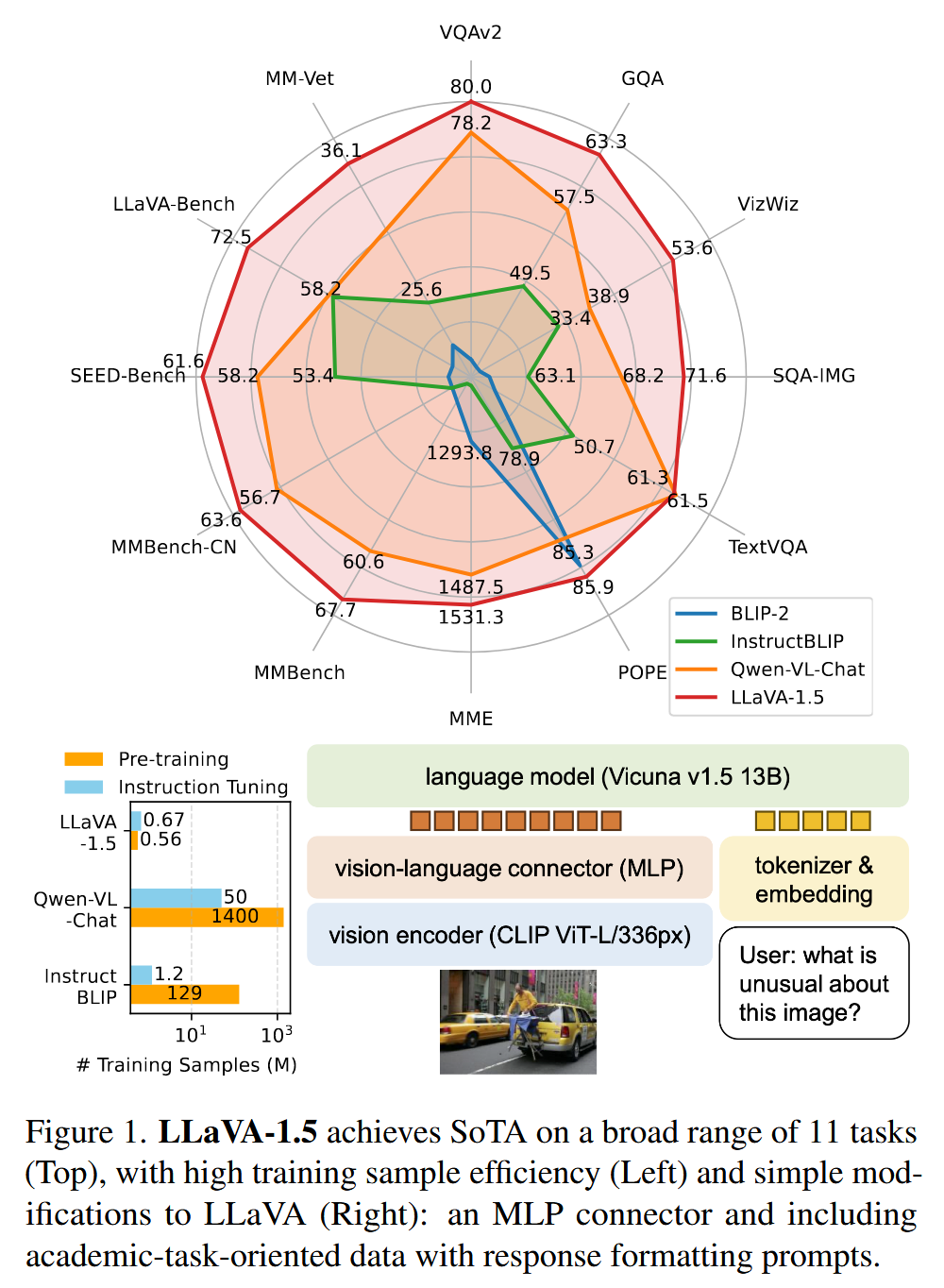
LLaVA-1.5 [CVPR’24]
paper: Improved Baselines with Visual Instruction Tuning
- arXiv:2310.03744v2 [cs.CV] 15 May 2024
- CVPR’24 (highlight)

- LLaVA 对比 InstructBLIP/Qwen-VL
- LLaVA 预训练 了一个
MLP cross-modal connector,并 微调 connector 和 LLM- 数据:在学术任务相关数据上,如 VQA
- 不足:short-form answers (e.g. single-word)
- InstructBLIP or Qwen-VL 预训练 了一个
visual resamplers (e.g. Qformer),并只 微调 instruction-aware Qformer- 数据:在数亿(hundreds of millions, 129M, InstructBLIP) or 甚至数十亿(even billions, 1.4B, Qwen-VL) 的 image-text paired 数据上
- 不足:long-form conversation (overfit short-form)
- LLaVA 预训练 了一个
- 改进模型架构:对LLaVA的简单修改
- Visual Encoder:
CLIP-ViT-L-336px(the highest resolution available for CLIP) - Vision-Language Connector: MLP projection (从 1-layer MLP 变成
2-layer MLP)
- Visual Encoder:
- 一些开放问题:
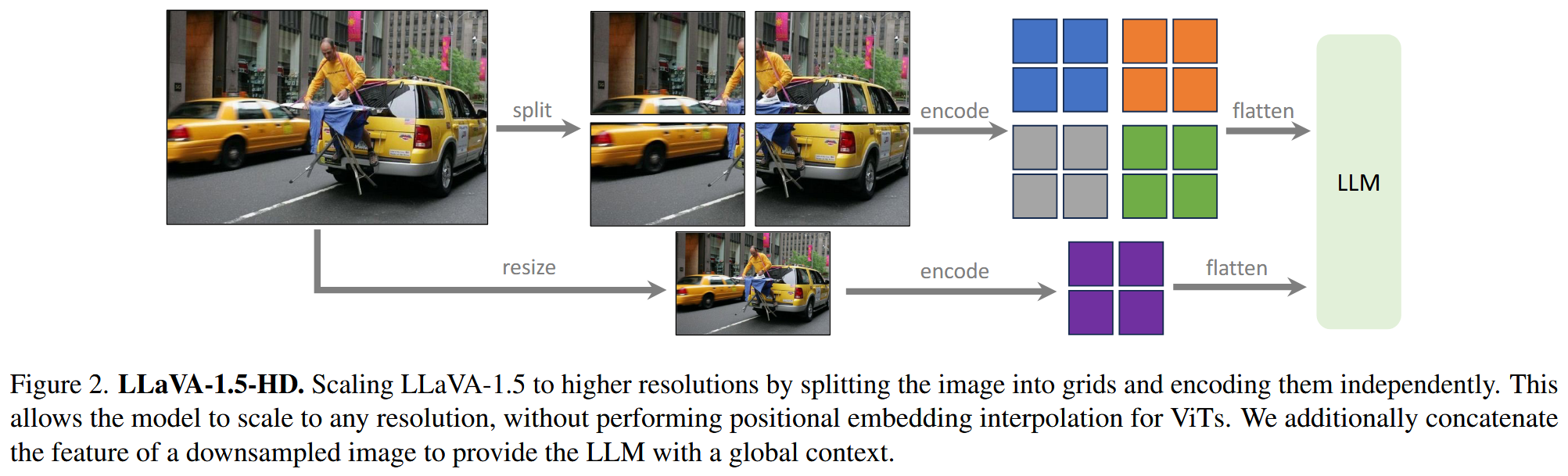
- Scaling to high-resolution image inputs | 兼容更高分辨率
- 采用 “split-encode-merge” 操作(训练得到
LLaVA-1.5-HD模型)
- 采用 “split-encode-merge” 操作(训练得到
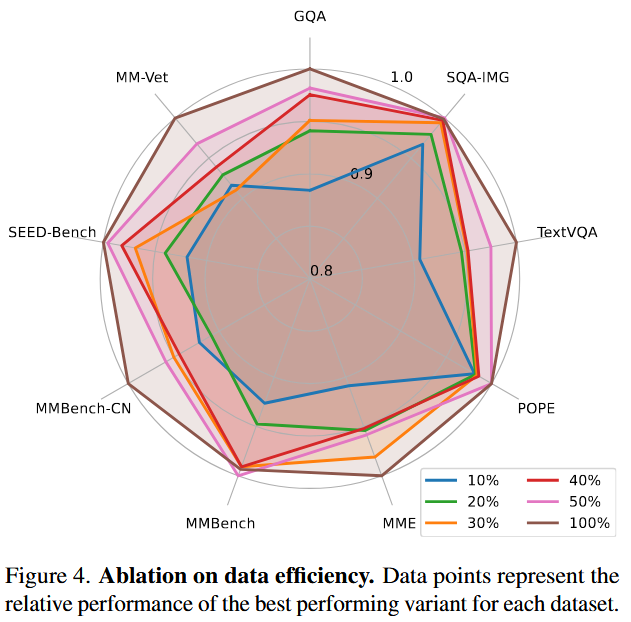
- Data efficiency | 训练数据效率
- 通过随机下采样训练集来提高数据效率(尝试下采样率0.1-0.5),证实了和其他多模态模型一样,具有 less-is-more benefit

- 发现下采样为原始数据的50%时,模型在full dataset上保持原始表现的98%
- 发现下采样为原始数据的30%时,模型的表现依然稳定
- 通过随机下采样训练集来提高数据效率(尝试下采样率0.1-0.5),证实了和其他多模态模型一样,具有 less-is-more benefit
- Hallucination in LMMs | 幻觉问题
- model的hallucination 可能来自于 训练集的errors或hallucination
- 当input的resolution变高,幻觉减少
- 需要 【更详细的data annotation】 和 【正确处理信息的model】
- Compositional capabilities | 组合能力(1+1>2)
- 证据:
- ShareGPT data 同时促进了 multimodal multilingual capability
- academic-task-oriented datasets 同时促进了 visual groundness 能力
- 问题:对于需要一定能力组合的某些task,仍然难以实现理想的表现
- 例如能够正确回答VQA中某个对象的属性,不能保证在整个图像的详细说明中准确描述该对象属性
- 此外,与某些外语(例如韩语)进行对话的能力仍然落后。
- 证据:
- Scaling to high-resolution image inputs | 兼容更高分辨率
- 模型大小:13B(default),7B
- 训练成本:仅用单机8张A100,~1 day
LLaVA-NeXT/LLaVA-1.6
https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/llava_next
2024.01.03LLaVA-NeXT: Improved reasoning, OCR, and world knowledge2024.04.30LLaVA-NeXT: A Strong Zero-shot Video Understanding Model2024.05.10LLaVA-NeXT: Stronger LLMs Supercharge Multimodal Capabilities in the Wild2024.05.25LLaVA-NeXT: What Else Influences Visual Instruction Tuning Beyond Data?2024.06.16LLaVA-NeXT: Tackling Multi-image, Video, and 3D in Large Multimodal Models
LLaVA-OneVision
2024.08.05LLaVA-OneVision: Easy Visual Task Transfer
LLaVA-Video
LLaVA-Critic
Qwen-VL系列
- blog: https://qwenlm.github.io/
- 参考资料:
Qwen-VL
paper: Qwen-VL: A Versatile Vision-Language Model for Understanding, Localization, Text Reading, and Beyond
- arXiv:2308.12966v3 [cs.CV] 13 Oct 2023
- blog: Qwen-VL全新升级!
- github: https://github.com/QwenLM/Qwen-VL
Qwen2-VL
paper: Qwen2-VL: Enhancing Vision-Language Model’s Perception of the World at Any Resolution
- arXiv:2409.12191v2 [cs.CV] 3 Oct 2024
- blog: Qwen2-VL: 更清晰地看世界
- github: https://github.com/QwenLM/Qwen2-VL
Qwen2.5-VL
report: Qwen2.5-VL Technical Report
- arXiv:2502.13923v1 [cs.CV] 19 Feb 2025
- blog: Qwen2.5 VL!Qwen2.5 VL!Qwen2.5 VL!
- github: https://github.com/QwenLM/Qwen2.5-VL
InternVL系列
InternVL
InternVL1.5
InternVL2.5
InternVL2.5-MPO
InternVL3
DeepSeek-VL系列
DeepSeek-VL
DeepSeek-VL: Towards Real-World Vision-Language Understanding
DeepSeek-VL2
DeepSeek-VL2: Mixture-of-Experts Vision-Language Models for Advanced Multimodal Understanding
Benchmark
Leaderboard
司南 OpenCompass
- Title: 多模态(Multimodal) 及 多模态大语言模型(MLLMs) 学习笔记
- Author: LeoJeshua
- Created at : 2025-05-19 11:31:00
- Updated at : 2025-07-25 23:46:56
- Link: https://leojeshua.github.io/Multimodal/Multimodal/
- License: This work is licensed under CC BY-NC-SA 4.0.