LLMs(Large Language Models) 学习笔记
信息收集
参考推文
- 公众号:全球名校LLM大语言模型经典课程自学指南
- 公众号:GitHub上41.3k颗星的2025年最新免费LLM课程
- 公众号:大神Karpathy亲授!最新LLM入门视频课!
- 斯坦福在线课程:人工智能研究生课程清单
资料总结
LLM全栈(课程视频)
Stanford CS224n: NLP with DL
Stanford CS25: Transformers United V5
CMU 11-711: Advanced NLP
普林斯顿 COS 597R:Deep Dive into LLM
- page: https://princeton-cos597r.github.io/
- vedio: 未公开
Andrej Karpathy (ps: 师从李飞飞,斯坦福cs231n设计者,openai联创,特斯拉自动驾驶系统高级总监)
- 课程计划(未上线):LLM101n
- 手搓GPT: NanoGPT
- youtube主页:https://www.youtube.com/@AndrejKarpathy
- 2025/02/06 Deep Dive into LLMs like ChatGPT
This is a general audience deep dive into the Large Language Model (LLM) AI technology that powers ChatGPT and related products. It is covers the full training stack of how the models are developed, along with mental models of how to think about their “psychology”, and how to get the best use them in practical applications. I have one “Intro to LLMs” video already from ~year ago, but that is just a re-recording of a random talk, so I wanted to loop around and do a lot more comprehensive version.
- 时长:3h31min
- 全面覆盖了 LLM 的完整训练堆栈,从模型的开发过程,到如何建立理解其 “心理学” 的心智模型,再到如何在实际应用中最大化其效用,都进行了细致的讲解。
- 本次的新视频是一次更为全面和深入的尝试,旨在更完整地呈现 LLM 技术的全貌。(一年前发布的 “LLMs 导论” 仅为一次随机演讲的重新录制,之前的导论视频仍可作为补充,因为它更深入地探讨了其他主题,例如 LLM 操作系统和 LLM 安全。)
- 2025/02/28 How I use LLMs
The example-driven, practical walkthrough of Large Language Models and their growing list of related features, as a new entry to my general audience series on LLMs. In this more practical followup, I take you through the many ways I use LLMs in my own life.
- 时长:2h21min
- 笔记:「听课 - Andrej Karpathy」 我如何使用大语言模型
- 2025/02/06 Deep Dive into LLMs like ChatGPT
Jay Alammar (Co-authors of “Hands-On Large Language Models” | 《动手学LLMs》的合著者)
- The Illustrated Transformer
- deeplearning.ai: How Transformer LLMs Work
- 1 Hour 35 Minutes (短期课程)
- 13 Video Lessons
- 3 Code Examples
- Instructors: Jay Alammar, Maarten Grootendorst
- 基础知识,包括Bag-of-Words, (word) embedding, attention, transformers, tokenizers, self-attention, MoE等知识点
LLM全栈(文本资料)
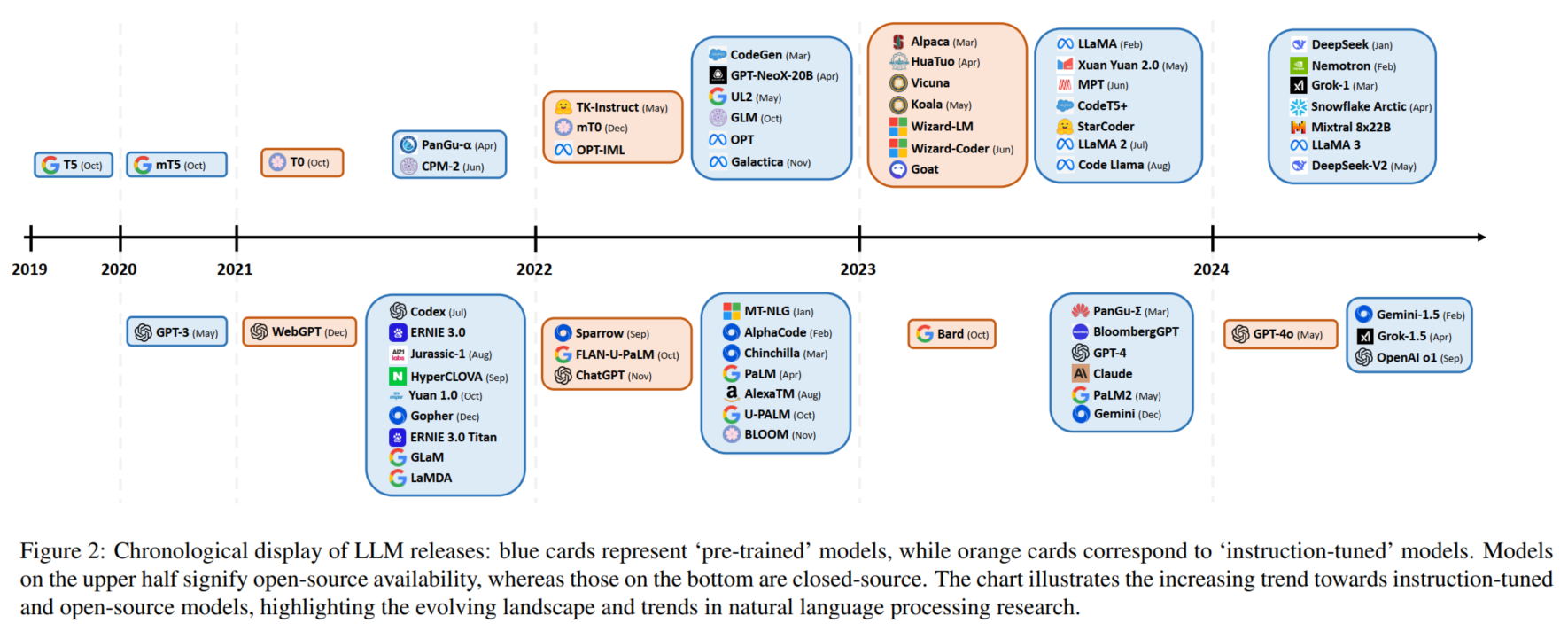
- Paper: “A Comprehensive Overview of Large Language Models”
- pdf: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2307.06435
- Submitted on 12 Jul 2023 (v1), last revised 17 Oct 2024 (this version, v10)
- 包括
Deepseek/Deepseek-V2/Grok-1/Grok-1.5/Gemini-1.5/OpenAI-o1等近期模型 - 正文35页,带引用47页


- Github: mlabonne/llm-course

- Book: “LLM Engineer’s Handbook: Master the art of engineering large language models from concept to production”(Paperback – 22 October 2024)
- Roadmap for Scientist:

- Roadmap for Engineer:

- DataWhale
- 基础知识:《大模型基础:一文了解大模型基础知识》
- 应用开发:《动手学大模型应用开发》
- 手撕架构:《大模型白盒子构建指南》

本项目是一个从原理出发、以“白盒”为导向、围绕大模型全链路的“手搓”大模型指南,旨在帮助有传统深度学习基础的读者从底层原理出发,“纯手搓”搭建一个清晰、可用的大模型系统,包括大模型本身、RAG 框架、Agent 系统及大模型评估体系。本项目将从基础原理出发,深入剖析每一个技术点并附以完整的代码实现,以细致讲解和代码注释帮助读者独立复现大模型核心部分,并在复现中实现对大模型的深入理解与掌握。
- 部署&微调:《开源大模型食用指南》

《开源大模型食用指南》针对中国宝宝量身打造的基于Linux环境 快速微调(全参数/Lora)、部署 国内外开源大模型(LLM)/多模态大模型(MLLM)教程。
- 进阶:Happy-LLM (pdf下载 / 在线阅读)
很多小伙伴在看完 Datawhale开源项目:self-llm《开源大模型食用指南》后,感觉意犹未尽。于是我们(Datawhale)决定推出《Happy-LLM》项目,旨在帮助大家 深入理解LLM的原理和训练过程。
提示词工程
分布式训练
- 跟李沐学AI:分布式训练【动手学深度学习v2】
- Lil’Log: How to Train Really Large Models on Many GPUs?
- 发布于2021-09-25, 更新于2022-06-10
- https://lilianweng.github.io/posts/2021-09-25-train-large/
- 训练并行性:单卡的主要瓶颈是 GPU内存不够,无法训练超大型神经网络
- 数据并行 (Data Parallelism, DP)
- Naive DP: 将相同的模型权重复制到多个worker中,并分配给每个worker一小部分数据,同时进行处理。
- 当模型太大无法装入一台worker时,将未使用的参数卸载回 CPU,以使用有限的 GPU 内存。
- 数据交换传输应在后端进行,并且不会干扰训练计算。
- 当每个minibatch结束时,worker需要同步
梯度或权重以避免过时。- 批量同步并行 | Bulk synchronous parallels (BSP)
- worker在每个minibatch结束时同步数据。(停止并等待其他机器发送梯度)
- 异步并行 | Asynchronous parallel (ASP)
- 每个 GPU 工作器都异步处理数据,无需等待或停顿。
- 很可能使用过时的权重,从而降低统计学习效率。
- 尽管它增加了计算时间,但可能不会加快训练收敛时间。
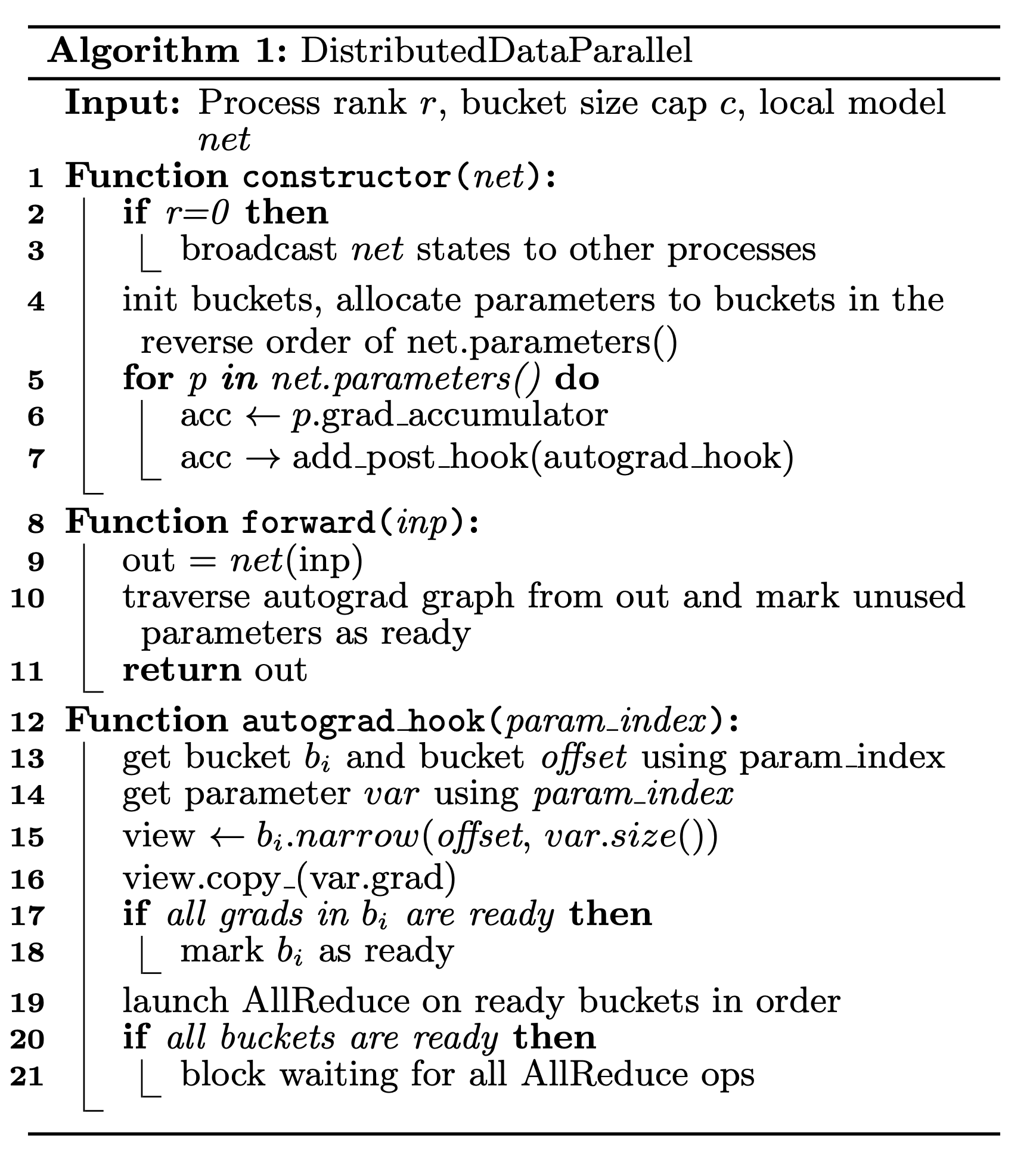
- 梯度累计 | “gradient accumulation” in Distribution Data Parallel (DDP)
- 折中方案,每 x iterations 全局同步一次梯度

- Naive DP: 将相同的模型权重复制到多个worker中,并分配给每个worker一小部分数据,同时进行处理。
- 模型并行 (Model Parallelism, MP)

- (动机)旨在解决 “模型权重无法放入单个节点” 的情况,模型参数分布在多台机器上。
- (优点)MP 仅在一个worker上分配一小部分模型参数,因此内存使用量和计算量均有所减少。
- (方法)由于深度神经网络通常包含一堆垂直层,因此 按层拆分大型模型 似乎很简单,其中 一小组连续的层 被分组到一个工作器上的一个分区中。
- (不足)然而,通过具有顺序依赖性的多个此类worker运行每个数据批次的简单实现,会导致 等待时间的巨大泡沫 和 计算资源的严重利用不足。
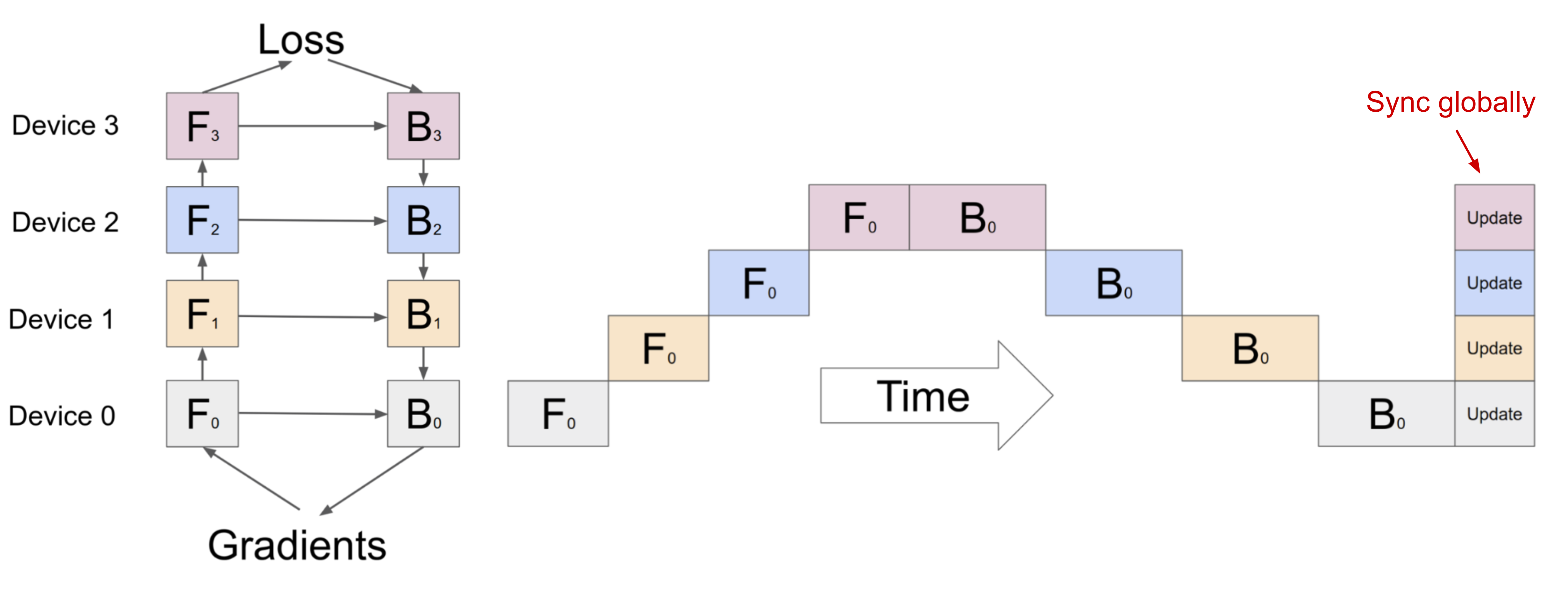
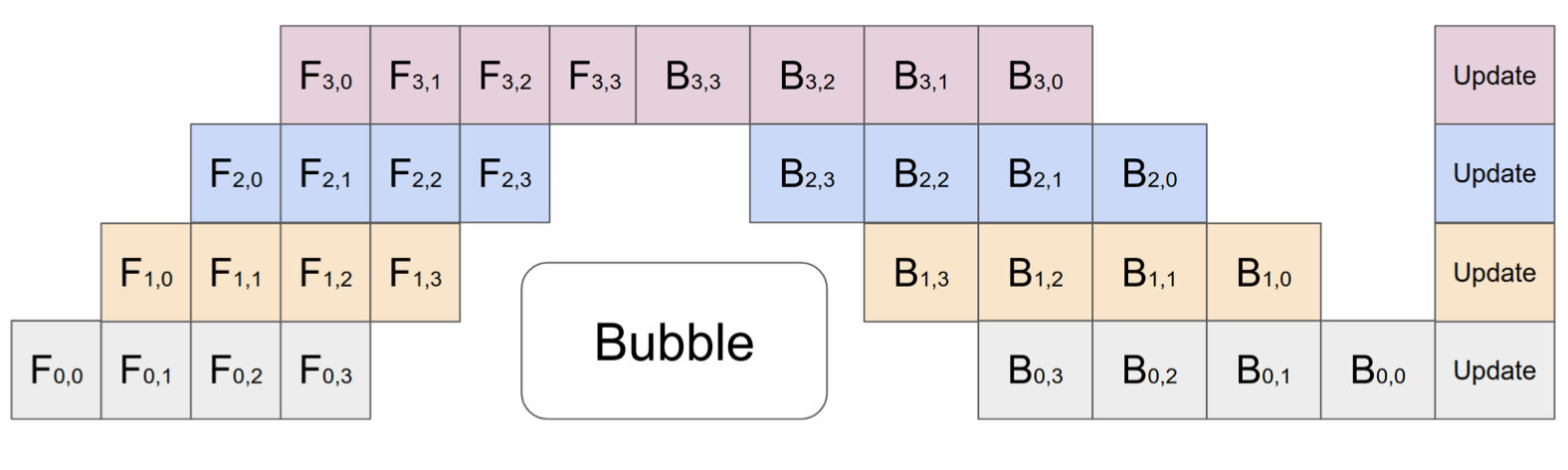
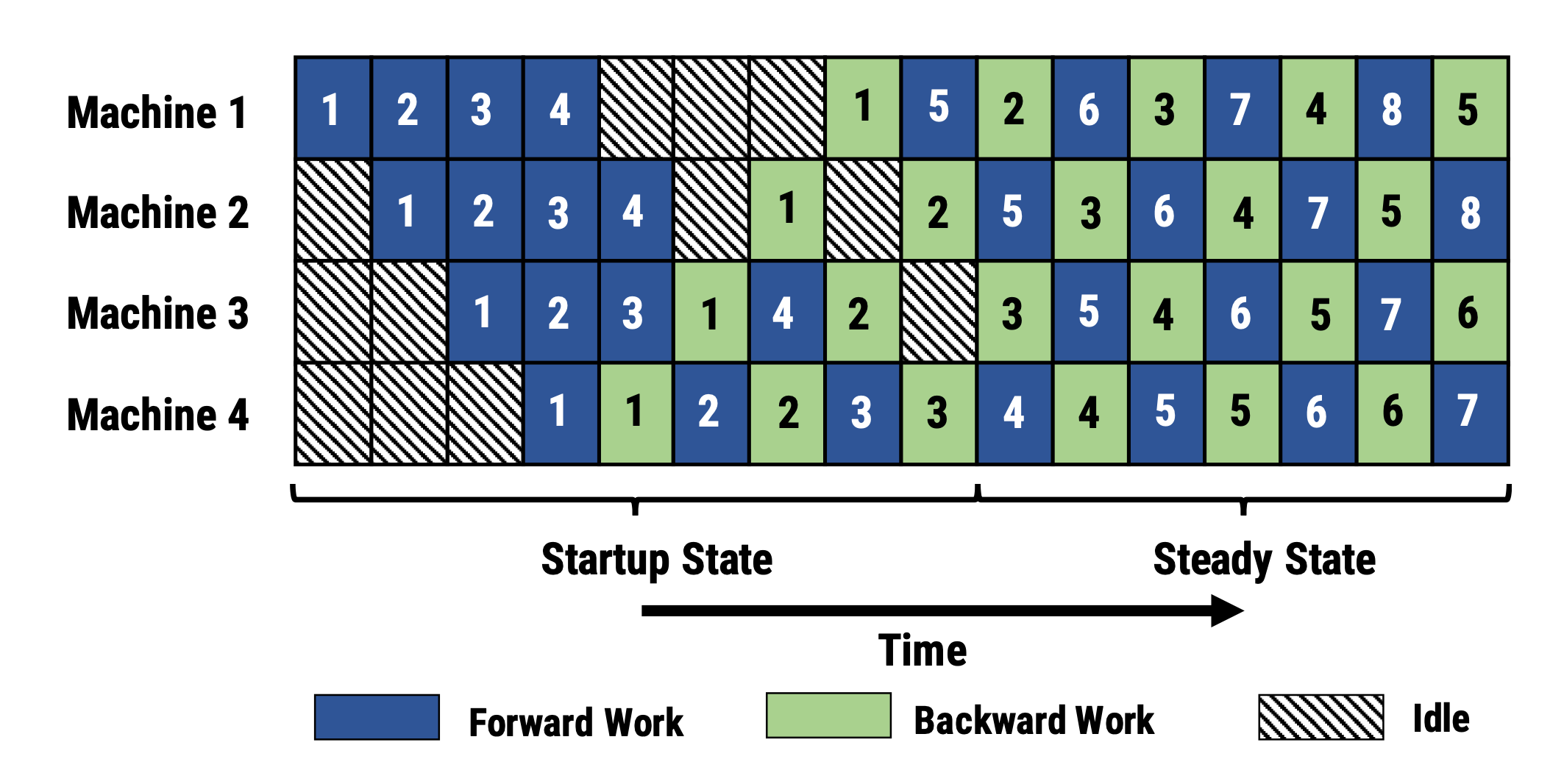
- 流水线并行 (Pipeline parallelism, PP)

- 将模型并行与数据并行相结合,以减少低效的时间“泡沫”。
- 主要思想是将一个小批次拆分为多个微批次,并使每个阶段worker能够同时处理一个微批次。
- 请注意,每个微批次都需要两次传递,一次向前,一次向后。worker间通信仅传输激活(向前)和梯度(向后)。这些传递的调度方式和梯度的聚合方式因方法而异。
- 【分区(worker)的数量】也称为 流水线深度
PipeDream安排每个worker交替处理前向和后向传递(1F1B)
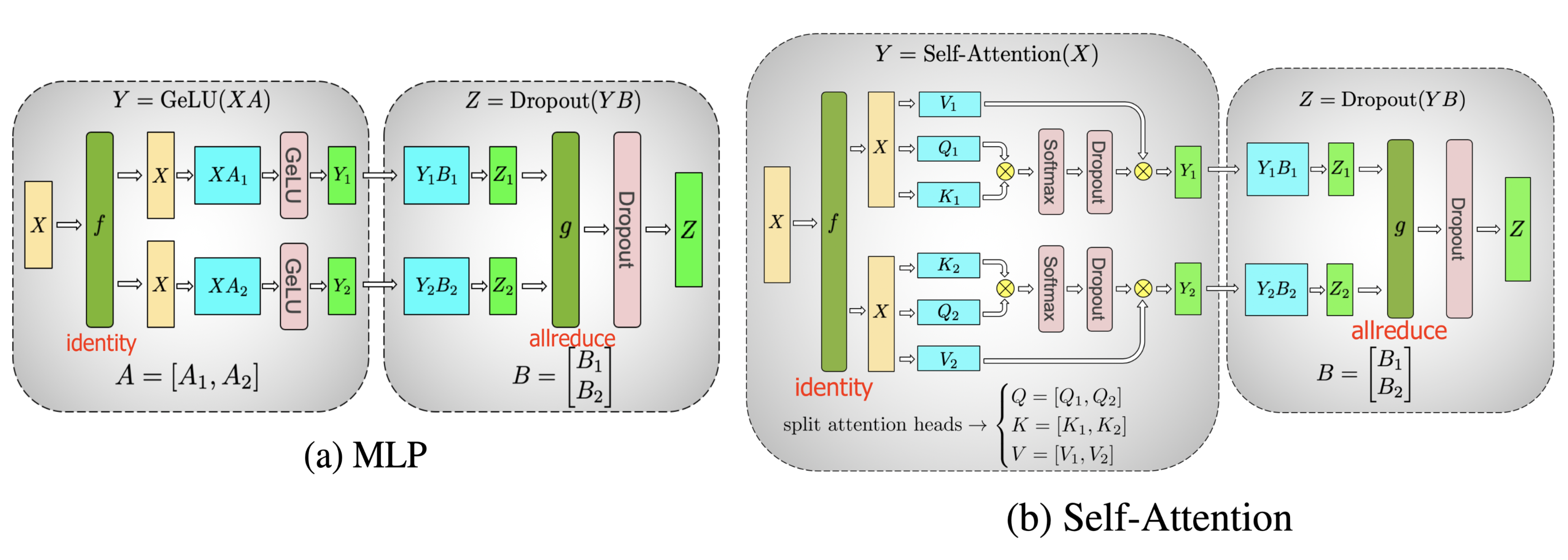
- 张量并行 (Tensor Parallelism, TP)
- 模型并行和流水线并行都垂直分割模型。另一方面,我们可以在多个设备上 水平划分 一次【张量运算】,这称为张量并行 (TP)。

- 模型并行和流水线并行都垂直分割模型。另一方面,我们可以在多个设备上 水平划分 一次【张量运算】,这称为张量并行 (TP)。
- 数据并行 (Data Parallelism, DP)
LLM安全
- “Foundational Challenges in Assuring Alignment and Safety of Large Language Models” | LLM在“对齐”和“安全”上面临的基本挑战
- page: https://llm-safety-challenges.github.io/
- pdf: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2404.09932
Abstract: This work identifies 18 foundational challenges in assuring the alignment and safety of large language models (LLMs). These challenges are organized into three different categories: scientific understanding of LLMs(1.对LLM的科学理解), development and deployment methods(2.开发和部署方法), and sociotechnical challenges(3.社会&技术挑战).
Based on the identified challenges, we pose 200+, concrete research questions.
Models
LLaMA系列
- web: https://www.llama.com/
- Meta AI
- models:
LLaMA-1 系列:
- Meta于2023年2月发布了LLaMA-1,包括7B、13B、30B和65B四个参数量版本。
- 这些模型在超过1T token的语料上进行了预训练,其中最大的65B参数模型在2,048张A100 80G GPU上训练了近21天。
- LLaMA-1因其开源性和优异性能迅速成为开源社区中最受欢迎的大模型之一。
LLaMA-2 系列:
- 2023年7月,Meta发布了LLaMA-2,包含7B、13B、34B和70B四个参数量版本,除了34B模型外,其他均已开源。
- LLaMA-2将预训练的语料扩充到了2T token,并将模型的上下文长度从2,048翻倍到了4,096。
- 引入了分组查询注意力机制(Grouped-Query Attention, GQA)等技术。
LLaMA-3 系列:
- 2024年4月,Meta发布了LLaMA-3,包括8B和70B两个参数量版本,同时透露400B的LLaMA-3还在训练中。
- LLaMA-3支持8K长文本,并采用了编码效率更高的tokenizer,词表大小为128K。
- 使用了超过15T token的预训练语料,是LLaMA-2的7倍多。
LLaMA 1 (2023.02)
LLaMA: Open and Efficient Foundation Language Models
- arXiv: 2302.13971v1 [cs.CL] 27 Feb 2023
- 核心Idea:
- 计算成本重要性:推理时 > 训练时
- 因此 对于一定参数量的模型,用更多data训练出更好的表现(同样表现的下的模型更小)
- 训练成本变大
- 推理成本变小 ⭐
- 数据集大小:1.4T tokens
- 模型大小:
- 7B
- 13B(比175B的GPT-3表现好)
- 33B
- 65B(对标Chinchilla-70B和PaLM-540B)
- 训练成本(65B):
- 2048张A100(80G of RAM)
- 21 days
- 380 tokens/sec/GPU
Approach
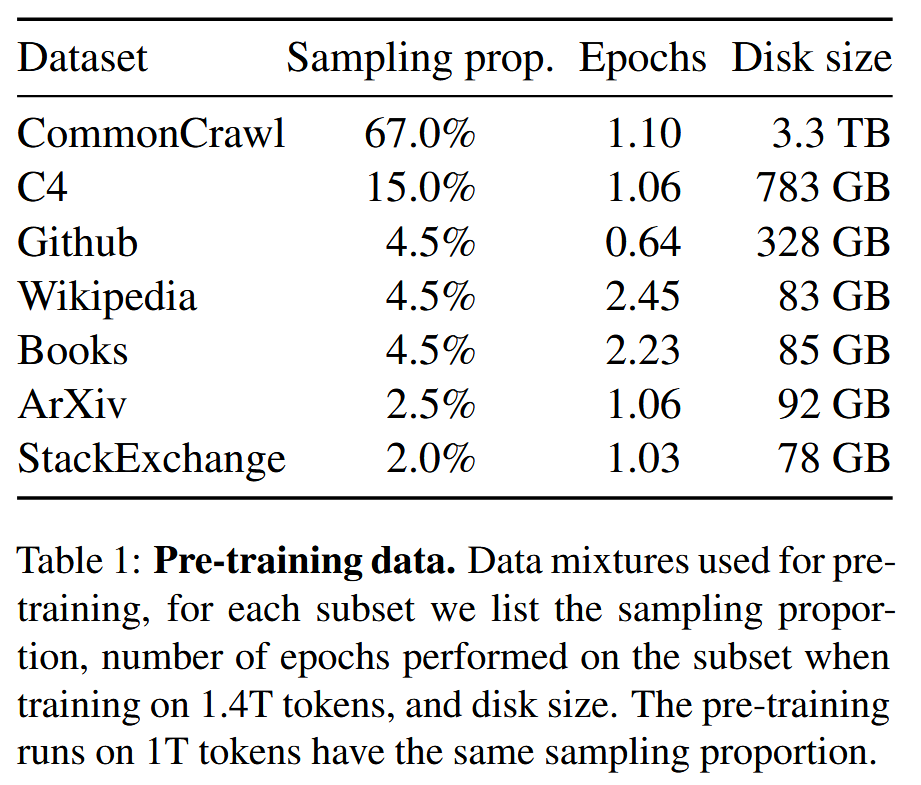
Pre-training Data
- 数据集总tokens:1.4T
- 除了Wikipedia和Books的数据(2个epoch),大多token在训练中只用一次(1个epoch)
Architecture ⭐
基于transformer架构,并借鉴之前一些工作的改进方案
- Pre-norm & RMSNorm
- 借鉴自 GPT-3,替换 Post-norm 和 LayerNorm
- SwiGLU activation function
- 借鉴自 PaLM,替换 ReLU
- a dimension of
instead of as in PaLM
- Rotary Position Embeddings (RoPE)
- 借鉴自 GPTNeo,替换 absolute positional embeddings
不同size的模型的超参细节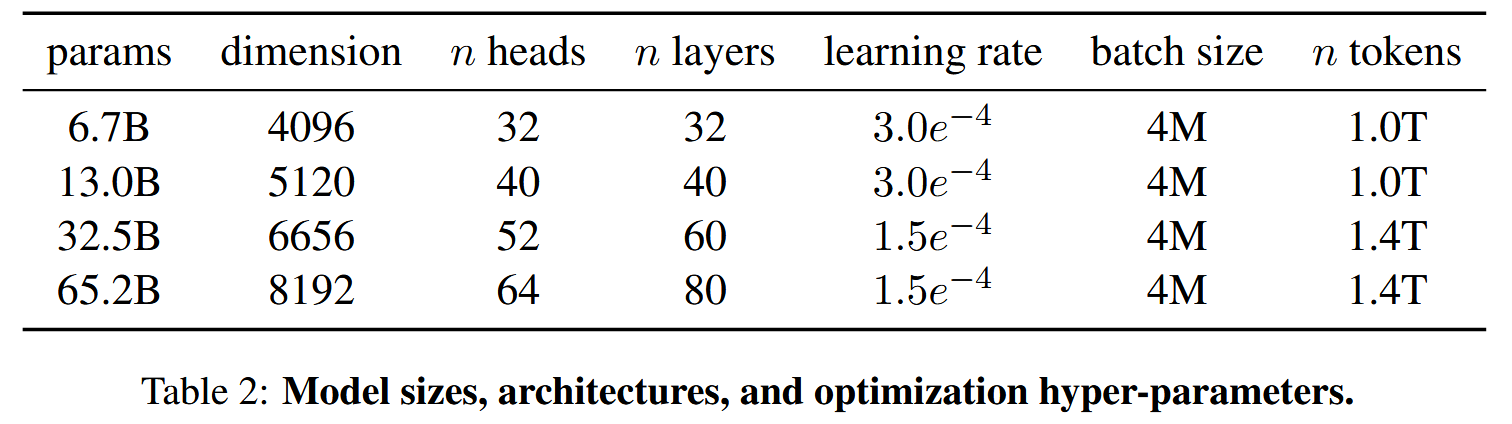
Optimizer
- 标准优化器: AdamW optimizer(β1 = 0.9, β2 = 0.95)
- a cosine learning rate schedule | 余弦学习率策略
- 最终学习率降至最大学习率的10%
- weight decay: 0.1
- gradient clipping: 1.0
- warmup steps: 2000
- learning rate和batch size也随模型大小而改变(见Table 2)
Efficient implementation
高效实现模型计算/训练时间
- 高效实现 causal Multi-Head Attention 来 减小runtime的memory
- 通过:不存储/计算 mask部分的 key/query scores
- 代码:available in
xformerslibrary
- 减少重复计算的activations数量
- 通过:保存activations that are expensive to compute(例如the outputs of linear layers)
- 代码:手工实现transformer layers的
backward function
- 减少model的内存占用
- 通过:model并行 / sequence并行
- 同时进行 activation计算 和 GPU通信
- 通过:
all_reduce操作
- 通过:
Main Results (TBD)
Instruction Finetuning (TBD)
Bias, Toxicity and Misinformation (TBD)
LLaMA 2 (2023.07)
LLaMA 3 (2024.04)
LLaMA 4 (2025.04)
The Llama 4 herd: The beginning of a new era of natively multimodal AI innovation
- Title: LLMs(Large Language Models) 学习笔记
- Author: LeoJeshua
- Created at : 2025-03-08 10:32:00
- Updated at : 2025-10-14 11:31:36
- Link: https://leojeshua.github.io/NLP/LLMs/
- License: This work is licensed under CC BY-NC-SA 4.0.